Access Network Technology: Introduction of GPON
What is GPON?
PON (Passive Optical Network) is a passive optical network with a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) structure. GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) is a kind of PON technology, which is composed of Gigabit-bit PON defined by ITU-T G.984.x series standard. The GPON network is shown in Figure 1.


OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is a convergence device for the terminal PON protocol placed at the local end.
· ONU (Optical Network Unit) is a user-side unit or terminal located in the client that provides various interfaces for users. OLT and ONU communicate with each other through the passive optical network ODN in the middle.
· ODN (Optical Distribution Network) is composed of passive optical devices such as optical fibers and one or more passive splitters. It provides an optical channel between OLT and ONU, plays the role of connecting OLT and ONU, and has high reliability.
Unpassing means that there are no devices such as optical amplifiers and regenerators in ODN, which saves the maintenance cost of outdoor active equipment.
Why choose GPON?
With the popularity of broadband services and the trend of optical copper, operators put forward higher and higher requirements for the transmission distance, bandwidth, reliability and low operating costs of the service. The following characteristics of GPON meet these requirements:
· Longer transmission distance: optical fiber transmission, the coverage radius of the access layer can reach up to 60km. It can solve the contradiction between distance and bandwidth of twisted pair.
· Higher bandwidth: the maximum downline rate per port is 2.5Gbit/s, and the maximum upline rate is 1.25Gbit/s. Meet the needs of users for high-bandwidth services, such as high-definition TV, live broadcast, etc.
QoS (Quality of Service) provides a flexible full-service experience: it provides traffic control that distinguishes between users and user services, ensures multi-user multi-service bandwidth, and provides differentiated services for different user businesses.
· Optical spectratr characteristics: After spectrinating, a local single optical fiber leads out multiple optical fibers to the household, which supports 1:128 spectrator ratio, which saves the backbone optical fiber resources and reduces operation and maintenance costs.
Basic concepts of GPON
GEM frame
The GEM (GPON Encapsulation Mode) frame is the smallest business carrying unit in GPON technology and the most basic data structure. All businesses should be encapsulated in the GEM frame and transmitted on the GPON line, identified by GEM Port.
Each GEM Port is identified by a unique Port ID and is globally allocated by OLT, that is, each ONU under each GPON port cannot use a GEM Port with a Port ID.
· GEM Port identifies the business virtual channel between OLT and ONU, that is, the channel carrying the business flow, similar to VPI (Virtual Path Identifier)/VCI (Virtual Channel) in the ATM virtual connection. Identifier) identification.
The GEM frame structure is shown.


PLI, Port ID, PTI and HEC (Header Error Check) constitute the GEM header, that is, the GEM frame header, which is mainly used to distinguish data in different GEM Ports. The specific meanings of each field are as follows:
· PLI: Indicates the length of the net charge of the data
· Port ID: the only GEM Port marked with different
· PTI: Net charge type identification, mainly to identify the status and type of the currently transmitted data, such as whether it is an OAM (Operation, Administration and Maintenance) message, whether the data has been transmitted, etc. Information
· HEC: Provide forward error correction coding function to ensure transmission quality
· Fragment Payload: Indicates the user data frame fragment
Take the mapping method of Ethernet business in GPON as an example to understand the role of GEM frames more intuitively. As shown.


· The GPON system parses the Ethernet frame and maps the data part directly to GEM Payload for transmission.
· The GEM frame will automatically encapsulate the header information.
· The mapping has a clear format and good compatibility.
T-CONT
T-CONT (Transmission Container) is a carrier for GPON upward. All GEM Ports are mapped to T-CONT, and OLT passes through DBA (Dynamic Bandwidth A). ssignment) The way of scheduling is up. T-CONT is the basis for the implementation of DBA. Through the bandwidth application of ONU to T-CONT and the authorization of OLT to T-CONT, the DBA of the upstream business flow of the entire GPON system is realized.
T-CONT is the most basic control unit of upline bandwidth in the GPON system. Each T-CONT is uniquely identified by Alloc-ID. Alloc-ID is assigned by each GPON port of OLT, that is, ONU under the same GPON port of OLT does not have the same T-CONT with the same Alloc-ID.
T-CONT includes five different types, and different types of T-CONT can be selected according to different types of business. Each T-CONT bandwidth type has specific QoS characteristics. QoS characteristics are mainly reflected in bandwidth guarantee, which are divided into fixed bandwidth, guaranteed bandwidth, guaranteed/maximum bandwidth, maximum bandwidth, and mixing mode (corresponding Type1 to Type5).
X in Table 1 represents the fixed bandwidth value, Y represents the guaranteed bandwidth value, Z represents the maximum bandwidth value, and – means that it is not involved.


- Type 1 (Fixed bandwidth). This type is usually used for sensitive services or specific ONUs. They can be TDM or VoIP services.
- Type 2 (Assured bandwidth). This type can be used for VoIP, MNG, and the same services.
- Type 3 (Non-assured bandwidth). This is the combination of assured and maximum bandwidth. It is usually used for VoIP services.
- Type 4 (Best-effort). It is maximum bandwidth, it is used for IPTV and HSI (High Service Internet).
- Type 5 (Hybrid mode). This type is a combination of all types.
Overview of GPON system
Introduction to GPON system
The mainstream PON technologies include BPON (Broadband Passive Optical Network), EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) and GPON. Due to the use of ATM packaging mode, BPON is mainly used for ATM business carrying, but as ATM technology has become outdated, BPON technology has also disappeared. EPON is an Ethernet passive optical network technology. GPON is a Gibbit passive optical network technology, which is the mainstream technology with the widest range of optical access at present.
The working principle of the GPON network is shown.
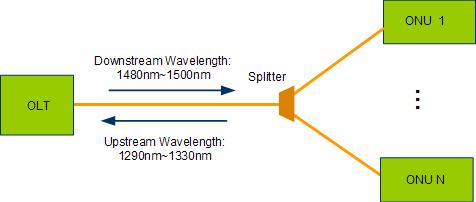

The GPON network uses a single optical fiber to connect OLT, spectrator and ONU, and the upstream and downstream use different wavelengths for data load. The upside adopts a wavelength in the range of 1290nm to 1330nm, and the downside adopts a wavelength in the range of 1480nm to 1500nm.
· The GPON system adopts the principle of wavelength division multiplexing to transmit data on the same ODN network through different wavelengths in the upper and lower rows, the data is transmitted by broadcasting, and the data is uploaded according to the time slot through TDMA.
GPON downline transmission
All data is broadcast from the OLT side to all ONUs, and ONU chooses to receive its own data and discards other data directly. The specific principles are shown.


Main features:
· Time Division Multiple Access
· Data is transmitted in your own time slot
· The optical signal is coupled at the splitter
· Conflict detection and avoidance through ranging
GPON networking application
GPON adopts passive optical transmission technology and is mainly used in FTTx solutions, including: FTTM (Fiber To The Mobility Base Station), FTTO (Fiber To The Office), FT TB (Fiber To The Building), FTTC (Fiber To The Curb), FTTD (Fiber To The Door), FTTW (Fiber To The WLAN), FT TH (Fiber To The Home) And D-CCAP (Distributed-Converged Cable Access Platform) Networking Scenarios Support Voice, Data, Video, Dedicated Line Access And Base Station Access Services The FTTx networking application is shown.


The common point of the FTTx network under the GPON access mode is that the end user’s data, voice and video signals are converted into ether messages after passing through ONU, and the GPON upline port of ONU is transmitted to OLT through optical fiber, and then forwarded from the OLT upline port to the upper IP network.
FTTH: OLT is connected to the ONT in the user’s home through ODN. FTTH networking is suitable for relatively scattered new high-end apartments or villas, providing higher-bandwidth services for high-end users.
· FTTB/FTTC: OLT is connected to the ONU of the corridor (FTTB) or the roadside (FTTC) through ODN, and ONU is connected to the end user. FTTB/FTTC networking is suitable for communities or office buildings with concentrated users, providing services with a certain bandwidth for ordinary users.
· FTTO: OLT is connected to the enterprise’s ONU through ODN, and ONU is connected to the end user. FTTO networking is suitable for enterprise networks, realizing the dedicated line business of TDM PBX, IP PBX, and enterprise intranet.
· FTTM: OLT is connected to ONU through ODN, and ONU is connected to the wireless base station. FTTM networking is suitable for the modification and expansion of mobile carrier network, and realizes the integration of fixed network and mobile network at the carrier level.
· FTTW: OLT is connected to ONU through ODN, and ONU is connected to AP to realize WLAN traffic back, which has become the future trend of Wi-Fi construction.
· D-CCAP: The D-CCAP construction scenario adopts a unified PON access platform and distributed deployment mode, which can meet the needs of household, enterprise and hot spot coverage. It is a new engine for HFC network to carry the three-network integration business.