[Abstract] With the advent of the digital era, the demand for the Internet continues to grow, and our home network is also evolving. Optical fiber to home (FTTH) has become the standard configuration for providing high-speed Internet connection, but with the development of technology, we have ushered in FTTR (optical fiber to room) technology, which represents the next major upgrade and technological evolution of the home network. The core concept of FTTR technology is to extend optical fiber coverage to users' rooms, further upgrade the traditional optical fiber to room to room, and provide a new Gigabit network coverage solution for the home network...
With the advent of the digital era, the demand for the Internet continues to grow, and our home network is also evolving. Optical fiber to home (FTTH) has become the standard configuration for providing high-speed Internet connection, but with the development of technology, we have ushered in FTTR (optical fiber to room) technology, which represents the next major upgrade and technological evolution of the home network. The core concept of FTTR technology is to extend optical fiber coverage to users’ rooms, further upgrade the traditional optical fiber to room, and provide a new Gigabit network coverage solution for the home network. This article will discuss the principles, advantages, future development trends and potential impact of FTTR technology in the home network.
I. Foreword
Before discussing FTTR (Fiber to The Room) in depth, let’s learn about FTTx. FTTx is the abbreviation of “Fiber To The x”, in which x represents the specific location where the optical fiber arrives and the optical network equipment installed at that location, and specifies the scope of services provided by these network equipment in the area. Specifically, the “x” of FTTx can include different abbreviations, representing different applications and scenarios.
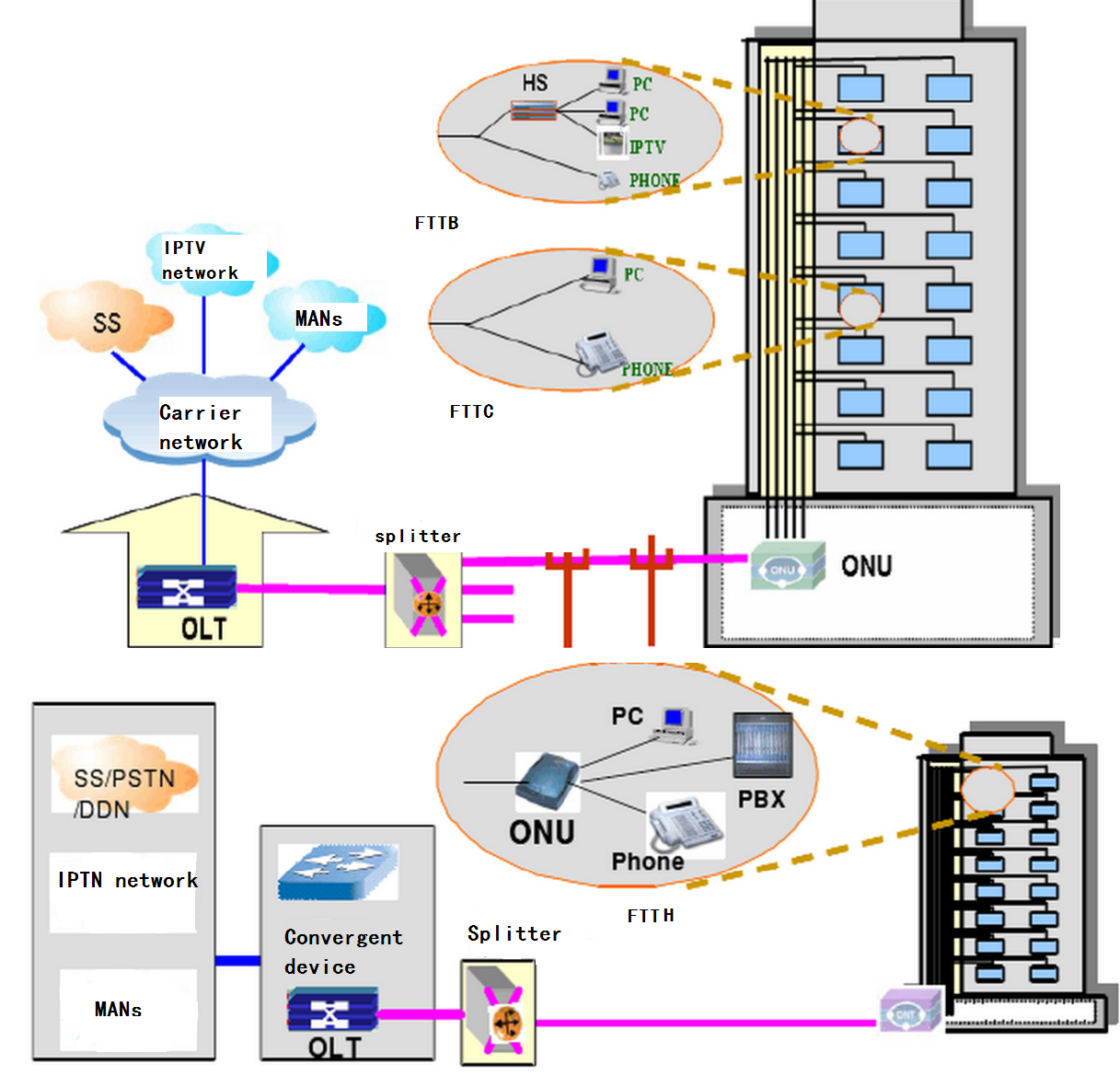
FTTH: In FTTH, “H” stands for “Home”, that is, optical fiber to the household. In this case, optical fiber is laid into the user’s home, and usually the modem or optical fiber terminal equipment is installed in the user’s home to provide Internet services. FTTH is suitable for individual families, and the service covers the whole family.
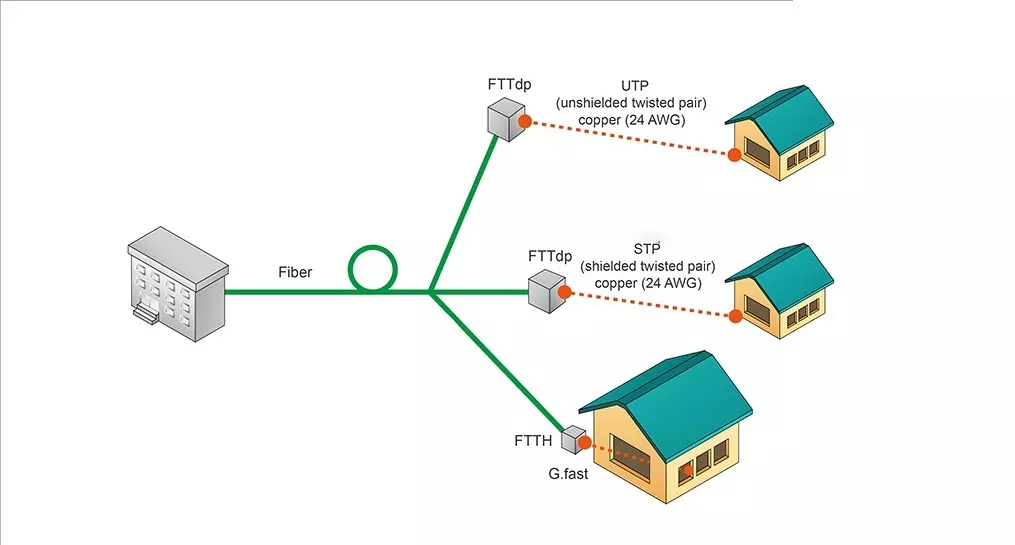

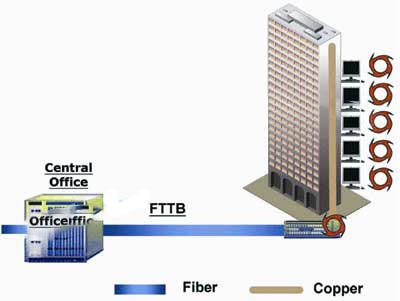
FTTB: “B” stands for “Building”, that is, optical fiber to the building. FTTB usually introduces optical fiber into multiple residential buildings or commercial buildings instead of single houses. In this case, the optical fiber usually reaches a central location in the building, and then transmits Internet services to each unit through internal wiring.

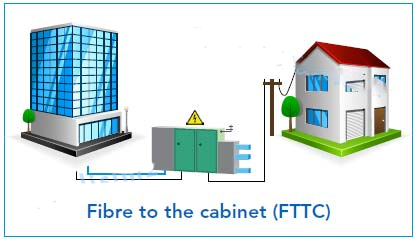
FTTC: “C” stands for “Curb”, that is, optical fiber to the roadside. In FTTC, optical fiber is laid to the roadside where the building is located, instead of directly entering the building. In this case, the last connection is usually done through the traditional copper wire (DSL) to transmit the signal to the user’s home.

FTTD: “D” stands for “Desk”, that is, optical fiber to the table. This application is usually found in the enterprise environment, and optical fiber is laid to each workbench to provide a high-speed network connection.

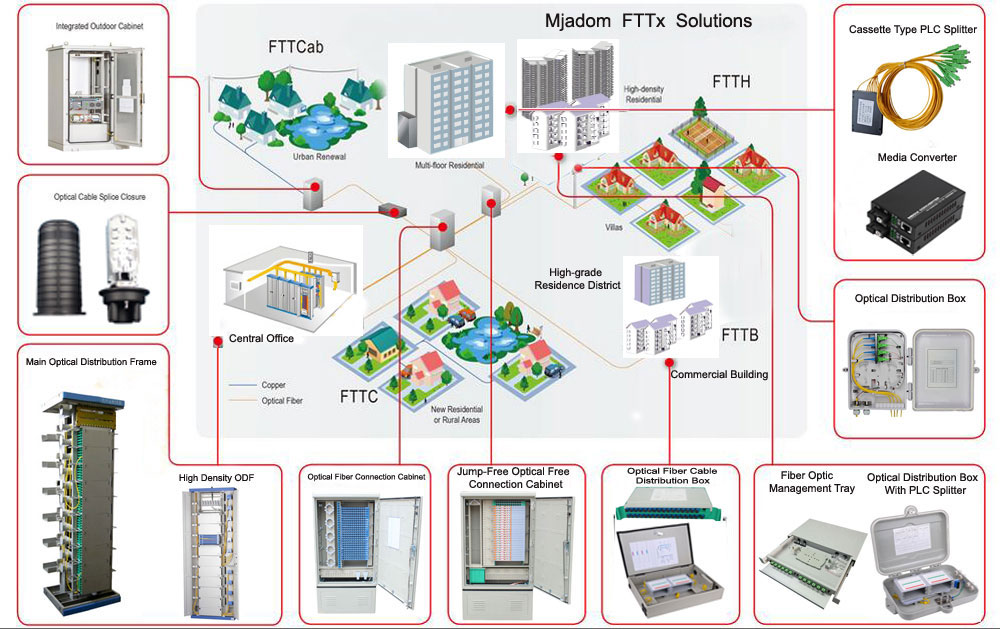
FTTX: This is a comprehensive term that refers to various applications and scenarios from various optical fibers to users, including all the situations mentioned above. It emphasizes the diversity of optical fiber as a transmission medium.

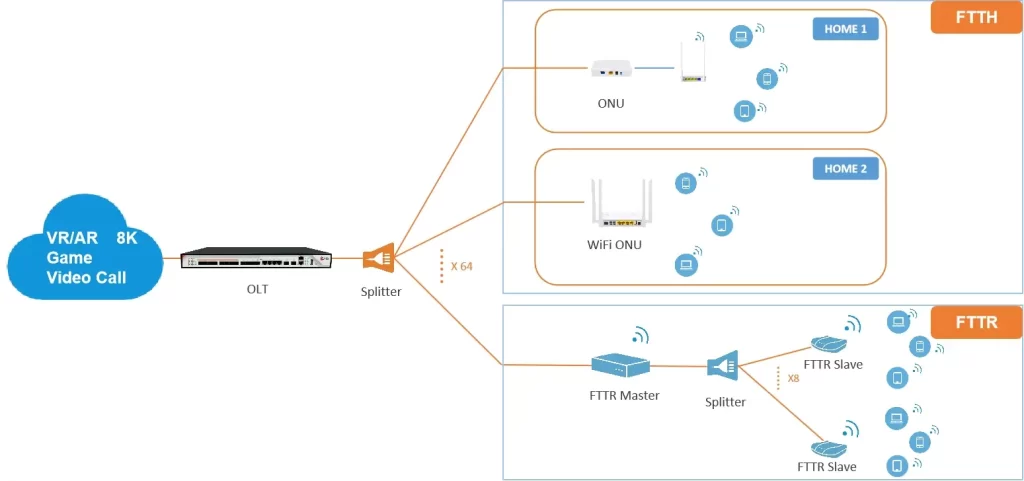
Now, let’s go back to FTTR. FTTR refers to replacing optical fiber with traditional network cables and laying optical fiber in each room, thus becoming a new coverage mode of home networks in the Gigabit era. In FTTR, each room has an optical fiber connection, and a modem is installed in the corresponding room to provide Internet services. This method upgrades the home internal network to a whole house-covered optical fiber network, solves the problem of indoor WiFi network coverage, provides gigabit bandwidth, and has the advantages of multi-terminal connection, full coverage upstairs and downstairs, and intelligent operation and maintenance.
II. Principle of FTTR technology
Full name in English: Fiber to The Room.
FTTR is an emerging home network coverage model. Its core principle is to extend the optical fiber network to remote nodes to better meet the needs of users. Traditional FTTH technology usually introduces optical fiber lines into users’ homes and terminates them at a single point indoors. However, FTTR adopts a more advanced method to introduce optical fiber into the user’s rooms, achieving wider coverage.
The main steps of FTTR technology include:
- Optical fiber network installation: Like traditional FTTH, FTTR also needs optical fiber network installation. This may involve burying optical fiber lines in the ground or erecting them on cable rods to transmit signals to various rooms.
- Optical Network Terminal (ONT): In each room, the optical fiber signal will be connected to ONT, which is the terminal device connected to FTTR. ONT is responsible for converting optical signals into electrical signals in order to connect to various devices of users.
- Indoor wiring: After ONT, the optical signal needs to be distributed to different rooms through indoor wiring. This usually requires the use of high-quality optical fiber home gateways to ensure the quality and stability of signal transmission.
- User equipment: Finally, users can connect to the optical fiber network through computers, smartphones, smart home devices and other devices to enjoy the high-speed connection of the Gigabit network.
III. Composition of FTTR network and key equipment
FTTR (Fiber to The Room) network is a complex system composed of different types of devices to achieve Gigabit network connection and full coverage WiFi. The following are the key components of the FTTR network:
- Main Light Cat: Main Light Cat is one of the core devices of the FTTR network. It connects OLT (Optical Line Terminal) up through XG(S)-PON or 10G EPON, and undertakes the task of Gigabit or 10G optical fiber to the household, that is, introducing the optical signal into the user’s home network. The main light cat usually integrates WiFi 6 routing function, making it an integrated device. It provides an interface to connect the optical path down and transmit the Internet signal to each room.
- From ONU: From ONU is a device that works in collaboration with the main light cat. It connects the main ONU up through indoor optical fiber, and then provides Internet services for terminal devices. From ONU plays a role in transmitting optical signals to each room, so as to realize the network covering the whole house.
- Optical splitter: Optical splitter is a device used to manage optical signals, which realizes the coupling, branching and distribution of optical signals. The optical splitter ensures that the optical signal can be transmitted correctly to each room and assigns the optical signal to provide services from ONU to the terminal equipment.
- Optical fiber: Optical fiber is the main medium of FTTR network, which is used to achieve long-distance optical signal transmission. Optical fiber has excellent signal transmission characteristics and can transmit high-bandwidth optical signals. When upgrading FTTR, high-quality optical fiber is usually required to ensure the quality and stability of the signal.
- Optical fiber panel: The optical fiber panel is used to complete the access and port output of dual-core optical fiber. Its design takes into account the bending radius requirements of the optical fiber to provide safety protection for the fiber core. The optical fiber panel plays a key role in connecting and distributing optical signals in the FTTR network.
IV. Why do you need FTTR?
4.1 Limitations of indoor WiFi
In many homes, the indoor WiFi network is connected to the router through the ONU (optical network unit), which is then covered by the router’s WiFi signal. Routers usually support 2.4G and 5G frequency bands. Although the 2.4G frequency band can support a speed of up to 300Mbps, the actual use effect is often unsatisfactory due to the high possibility of interference. Users’ high-bandwidth applications usually need to use the 5G band. However, the WiFi signal transmission capacity of the 5G band is weak, especially in the wall penetration. This brings great inconvenience to many users when applying with high bandwidth.
4.2 FTTR solutions
FTTR technology provides an innovative solution that introduces optical fiber into every room of the home and fundamentally solves the problem of indoor WiFi network coverage. FTTR lays optical fiber into each room, providing a powerful gigabit network connection. Such network connections far exceed traditional WiFi connections in terms of bandwidth and signal transmission. The ultra-gigabit WiFi network with good stability can cover every corner of the home, providing low latency, multi-connection, ultra-high speed and other features. This meets the high-quality network needs of the whole family, so that people can enjoy VR movies, VR games, 4K videos, real-time meetings and smooth online courses anytime and anywhere.
4.3 Achieve the balance of digital life
With the continuous evolution of the digital era, we increasingly rely on high-speed Internet connection to meet various needs, including entertainment, work, education, etc. The introduction of FTTR technology helps to build a stable digital life platform and eliminates the bottleneck of WiFi network. People can achieve a more easy balance between life and work and enjoy high-quality digital experience, which has become particularly important in the current society.
V. Advantages of FTTR technology
The introduction of FTTR technology brings multiple advantages, making it a powerful choice for future home network upgrades:

5.1 High bandwidth and fast Internet speed
The FTTR solution provides real gigabit bandwidth for each room. The main ONU is up through XGSPON or 10G EPON, and the maximum rate supports 10Gbps. Connect to the room from ONU through optical fiber, and support Gigabit network port and Wi-Fi 6. This method avoids the performance attenuation caused by Wi-Fi signals passing through the wall. The air port rate of Wi-Fi 6 can exceed Gigabit, providing real Gigabit bandwidth for each room. This means that users can enjoy multiple high-bandwidth applications at the same time without network congestion.
5.2 Advantagious characteristics of optical fiber
As a data transmission medium, optical fiber has many advantages, including softness, non-oxidation, non-corrosive, no electromagnetic interference, etc. The service life of optical fiber is up to 30 years, and a single deployment can benefit 30 years, which makes it a long-term reliable network connection. In addition, the bandwidth of optical fiber can continue to evolve to more than 100Gbps to meet the needs of high-bandwidth services in the future and ensure the sustainability and upgradeability of user investment.
5.3 Simple and beautiful layout
The problem of unsightly wiring may occur in the traditional wiring process, but FTTR whole house gigabit fiber solves this problem. It is compatible with light and dark line networking, with more beautiful lines, does not destroy the decoration style, and perfectly fits the home environment. This makes the network layout no longer a visual obstacle, but can be coordinated with home design and decoration, improving the aesthetics of the interior.
5.4 Seamless roaming and no-perception switching
FTTR technology provides the ability to roam seamlessly, so that the network connection will not be interrupted when users move between rooms. The main OTN is automatically connected, and the home Wi-Fi is unified in the main OTN, which can be automatically synchronized to the OTN. Dual-band automatic optimization ensures that the terminal equipment is connected with the optimal bandwidth carrying capacity. The seamless roaming function realizes signal switching between different access points in the home, ensuring business continuity.
5.5 Multi-terminal connection
FTTR supports the connection of up to 256 terminal devices, which is 8 times the maximum number of connections in the traditional network. This means that users can connect to various whole-house intelligent terminals, including computers, TVs, mobile phones, tablets, VR and other devices without worrying about network congestion.
5.6 Full coverage upstairs and downstairs
FTTR whole house gigabit fiber adopts a 10G OTN 1 to N mode to extend the fiber connection to every corner of the home. The optical fiber has strong transmission capacity, higher transmission rate and longer network cable life. This can also support 10 Gigabit uplinks and dynamically display wide technical signals to ensure that the whole family can enjoy a high-speed Internet connection upstairs and downstairs.
5.7 Intelligent operation and maintenance
The FTTR cloud management platform provides network visualization and manageable functions to help operators improve the user’s Wi-Fi experience, improve operation and maintenance efficiency, and reduce door-to-door visits. The platform can identify faults and performance problems, and provide suggestions for improvement, thus reducing users’ network problems. In addition, it can also identify user characteristics and provide more business opportunities for operators.
VI. Future development trend
FTTR technology represents one of the future development trends of home networks. With the continuous evolution of the digital era, our demand for high-speed Internet connection will continue to increase, and FTTR is expected to become one of the key technologies to meet these needs.
- Higher bandwidth: With the continuous increase of Internet applications, users’ demand for higher bandwidth will continue to grow. In the future, FTTR technology will provide higher bandwidth to meet users’ needs for large-traffic applications such as 4K/8K video, virtual reality and augmented reality.
- Smart home: With the popularization of smart home devices, FTTR will become a key technology to support smart home devices. It will ensure that these devices have a high-speed and stable Internet connection and improve the convenience and efficiency of family life.
- Integration of 5G and FTTR: The rise of 5G mobile communication technology and the integration of FTTR will become the future trend. 5G will provide higher mobile Internet speed, while FTTR will provide fixed broadband connection, which complements each other and provides users with more connection options.
According to IDATE’s estimate, by the end of 2025, the number of global FTTR users will reach 22 million. This shows that FTTR, as a future optical fiber connection technology, will be widely used worldwide. As more homes and businesses seek high-speed Internet connections, FTTR will continue to help operators develop high-quality broadband services.
The future prospects of FTTR are promising, especially in countries and regions where high-coverage optical fiber networks have been established. With the continuous evolution of technology and the growth of users’ demand for high-speed Internet, FTTR will become an important tool to meet these needs and provide users with a better network experience.