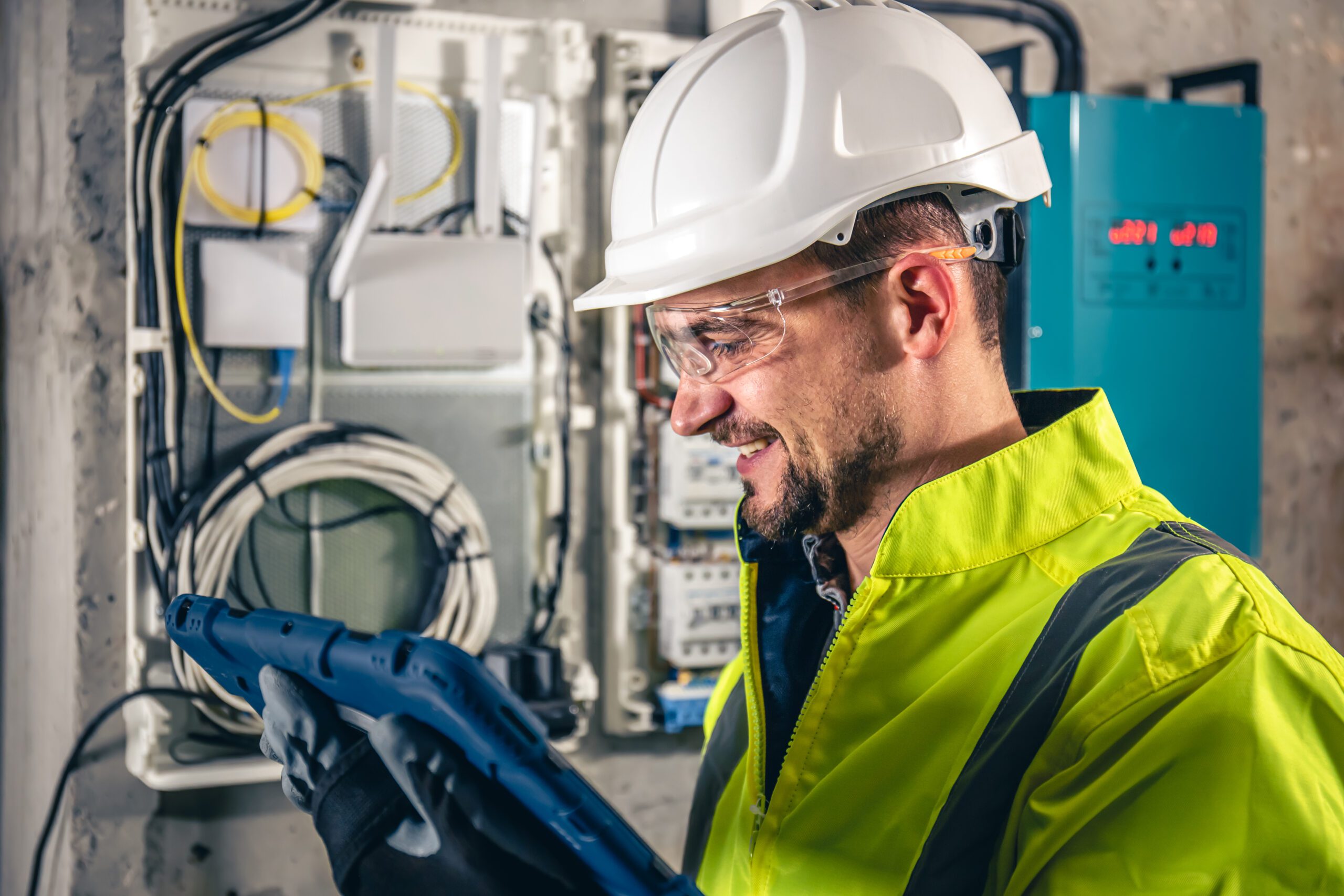
Basic Concepts
- Q: What is FTTH?
A: FTTH (Fiber To The Home) is a fiber optic cable network that provides high-speed internet directly to individual homes and businesses. - Q: How is FTTH different from traditional copper networks?
A: FTTH uses light signals through fiber optic cables instead of electrical signals through copper wires, offering much higher speeds and better reliability. - Q: What speeds can FTTH deliver?
A: FTTH can deliver symmetrical speeds from 100 Mbps up to 10 Gbps, depending on the service provider and technology used.
Installation and Infrastructure
- Q: How is FTTH installed to a home?
A: Installation involves running fiber optic cable from the nearest distribution point to the home, installing an ONT (Optical Network Terminal), and connecting it to the home router. - Q: What is an ONT?
A: An ONT (Optical Network Terminal) converts optical signals from fiber cables into electrical signals that can be used by home networking equipment. - Q: Does FTTH installation require digging?
A: Sometimes, but existing ducts and aerial installations can often be used to minimize disruption. - Q: How long does FTTH installation take?
A: Typical installation takes 4-8 hours for a single home, depending on complexity and existing infrastructure.
Technical Aspects
- Q: What is the maximum distance for FTTH?
A: FTTH can typically reach up to 20 kilometers from the central office without signal degradation. - Q: What is PON in FTTH?
A: PON (Passive Optical Network) is a point-to-multipoint architecture that uses passive splitters to serve multiple homes from a single fiber line. - Q: What are the different types of PON?
A: Common types include GPON, EPON, XG-PON, and NG-PON2, each offering different speeds and capabilities.
Performance and Quality
- Q: How reliable is FTTH?
A: FTTH is highly reliable as fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference and weather conditions. - Q: What affects FTTH performance?
A: Main factors include distance from the central office, quality of installation, and network equipment specifications. - Q: Does FTTH speed vary with distance?
A: Unlike copper networks, FTTH maintains consistent speeds over long distances within its specified range.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Q: How often does FTTH need maintenance?
A: FTTH requires minimal maintenance as fiber optic cables are durable and resistant to environmental factors. - Q: What are common FTTH problems?
A: Common issues include physical cable damage, dirty connectors, and equipment failures. - Q: How are fiber breaks detected?
A: OTDR (Optical Time Domain Reflectometer) testing can locate breaks and faults in fiber optic cables.
Cost and Economics
- Q: Why is FTTH installation expensive?
A: Costs include fiber optic cable, specialized equipment, skilled labor, and civil works for deployment. - Q: What is the typical lifespan of FTTH infrastructure?
A: Fiber optic cables can last 20-25 years or more with proper installation and maintenance. - Q: How does FTTH affect property value?
A: FTTH connectivity typically increases property value and attractiveness to buyers.
Security and Safety
- Q: Is FTTH more secure than copper networks?
A: Yes, fiber optic cables are more difficult to tap into and don’t emit electromagnetic signals. - Q: Are there health risks with FTTH?
A: No, fiber optic cables don’t emit radiation and are completely safe for residential use. - Q: How safe is the laser light in fiber cables?
A: The light is contained within the fiber and safety mechanisms prevent exposure during breaks.
Service and Support
- Q: What happens during a power outage?
A: FTTH equipment requires power to operate; backup power systems are recommended for continuous service. - Q: Can multiple services run on FTTH?
A: Yes, FTTH supports triple-play services: internet, telephone, and television simultaneously. - Q: How is FTTH bandwidth shared?
A: In PON networks, bandwidth is shared among users on the same splitter but maintains high speeds for all.
Future-Proofing
- Q: Can FTTH speeds be upgraded?
A: Yes, by upgrading end-point equipment without changing the fiber infrastructure. - Q: Will FTTH become obsolete?
A: No, fiber optic technology is considered future-proof with potential for much higher speeds. - Q: What’s next after FTTH?
A: Higher speed standards like 25G-PON and 50G-PON are being developed.
Environmental Impact
- Q: Is FTTH environmentally friendly?
A: Yes, fiber optic networks consume less energy and have a smaller carbon footprint than copper networks. - Q: Can FTTH cables be recycled?
A: Yes, though the process is different from copper cable recycling.
Installation Planning
- Q: What permits are needed for FTTH?
A: Usually requires local government permits, utility clearances, and sometimes homeowner association approval. - Q: Can FTTH be installed in old buildings?
A: Yes, though installation methods may need to be adapted for existing structure limitations. - Q: What space is needed for FTTH equipment?
A: Minimal space required: typically wall space for ONT and power outlet access.
Network Architecture
- Q: What is FTTH splicing?
A: The process of joining fiber optic cables together using fusion or mechanical splicing. - Q: What is the difference between active and passive FTTH?
A: Active networks use powered equipment at distribution points, while passive networks use unpowered optical splitters. - Q: What is an OLT in FTTH?
A: OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is the equipment at the service provider’s central office that manages fiber connections to customers.
Service Quality
- Q: What causes FTTH signal loss?
A: Main causes include poor splices, bent fibers, dirty connectors, and damaged cables. - Q: How is FTTH service quality measured?
A: Through metrics like signal strength, bit error rate, and optical power levels. - Q: What is acceptable latency for FTTH?
A: Typically less than 1ms for local connections and depends on distance for internet services.
Business Applications
- Q: How does FTTH benefit businesses?
A: Provides reliable high-speed connectivity for cloud services, video conferencing, and data transfer. - Q: Can FTTH support enterprise-level services?
A: Yes, with appropriate service level agreements and business-grade equipment. - Q: What is the difference between residential and business FTTH?
A: Business services often include higher speeds, better support, and stronger service level agreements.
Smart Home Integration
- Q: Can FTTH support smart home devices?
A: Yes, provides ideal bandwidth and reliability for multiple smart home devices. - Q: How many devices can FTTH support?
A: Practically unlimited devices within home network capacity. - Q: Does FTTH improve smart home performance?
A: Yes, provides low latency and high bandwidth needed for smart home automation.
Regulatory Compliance
- Q: What safety standards apply to FTTH?
A: Must comply with national telecommunications standards and safety regulations. - Q: Are there specific building codes for FTTH?
A: Yes, including fire safety ratings for indoor cables and installation requirements. - Q: What consumer protection applies to FTTH services?
A: Varies by country but typically includes service guarantees and consumer rights.
Rural Deployment
- Q: How is FTTH deployed in rural areas?
A: Often requires government subsidies and special construction techniques for long distances. - Q: What challenges exist for rural FTTH?
A: Include high cost per user, difficult terrain, and lower population density.
Emergency Response
- Q: How quickly can FTTH be repaired?
A: Depends on damage type but typically within 24-48 hours for standard breaks. - Q: What backup options exist for FTTH?
A: Include battery backup systems and cellular failover options. - Q: How are FTTH emergencies prioritized?
A: Based on number of affected users and service level agreements.
Installation Methods
- Q: What is micro-trenching for FTTH?
A: A installation method using narrow, shallow trenches to minimize disruption. - Q: Can FTTH be installed overhead?
A: Yes, using existing utility poles or dedicated aerial infrastructure. - Q: What is blown fiber installation?
A: Technique using compressed air to install fiber cables through ducts.
Testing and Certification
- Q: How is FTTH testing performed?
A: Using specialized equipment like OTDR, power meters, and fiber inspection tools. - Q: What certifications are needed for FTTH technicians?
A: Fiber optic certification and safety training required for installation and maintenance. - Q: How often should FTTH be tested?
A: Regular testing during installation, after repairs, and periodic preventive maintenance.
Performance Optimization
- Q: How can FTTH performance be optimized?
A: Through proper installation, regular maintenance, and equipment upgrades. - Q: What affects FTTH signal quality?
A: Includes fiber quality, connection cleanliness, and equipment calibration. - Q: How is FTTH bandwidth managed?
A: Through traffic shaping, quality of service settings, and network monitoring.
Weather and Environmental Factors
- Q: How does weather affect FTTH?
A: Minimal impact as fiber optic cables are weather-resistant. - Q: Can temperature affect FTTH?
A: Extreme temperatures can affect equipment but not fiber transmission. - Q: How is FTTH protected from lightning?
A: Through proper grounding and surge protection equipment.
Network Management
- Q: How is FTTH network monitored?
A: Using specialized software and monitoring systems for performance and faults. - Q: What is FTTH network redundancy?
A: Backup paths and systems to maintain service during failures. - Q: How is FTTH traffic prioritized?
A: Through quality of service settings for different types of data.
Service Upgrades
- Q: Can FTTH speed be upgraded without new cables?
A: Yes, often possible through equipment upgrades at endpoints. - Q: What determines upgrade capability?
A: Existing infrastructure quality and equipment compatibility. - Q: How often should FTTH be upgraded?
A: Based on technology advances and user demand, typically every 5-10 years.
Consumer Education
- Q: What should consumers know before getting FTTH?
A: Installation requirements, service options, and equipment needs. - Q: How can consumers maximize FTTH benefits?
A: Through proper home networking and understanding service features. - Q: What are common consumer misconceptions about FTTH?
A: Including cost assumptions and technical limitations.
International Standards
- Q: What international standards govern FTTH?
A: ITU-T and IEEE standards for fiber optic networks. - Q: How do FTTH standards vary globally?
A: Different countries may have specific requirements and specifications. - Q: What is international FTTH certification?
A: Standards for equipment and installation quality assurance.
Planning and Development
- Q: How is FTTH rollout planned?
A: Through demographic analysis, infrastructure assessment, and cost modeling. - Q: What factors influence FTTH deployment?
A: Population density, existing infrastructure, and economic factors. - Q: How is FTTH coverage determined?
A: Through geographic and demographic analysis of service areas.
Equipment Selection
- Q: How to choose FTTH equipment?
A: Based on performance requirements, compatibility, and cost considerations. - Q: What is minimum required equipment?
A: ONT, router, and appropriate cables and connectors. - Q: How to evaluate equipment quality?
A: Through certification, testing, and vendor reputation.
Professional Services
- Q: What professional services are needed?
A: Installation, maintenance, and technical support services. - Q: How to choose FTTH providers?
A: Consider coverage, service quality, and customer support. - Q: What support services are typical?
A: 24/7 technical support, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Cost Management
- Q: How to reduce FTTH costs?
A: Through efficient planning, bulk deployment, and infrastructure sharing. - Q: What ongoing costs exist?
A: Include maintenance, power consumption, and equipment updates. - Q: How to budget for FTTH?
A: Consider installation, equipment, and ongoing service costs.
Quality Assurance
- Q: How is FTTH quality assured?
A: Through testing, certification, and regular monitoring. - Q: What quality metrics matter?
A: Signal strength, bandwidth, latency, and reliability. - Q: How to maintain quality standards?
A: Regular testing, maintenance, and equipment updates.
Documentation
- Q: What documentation is needed?
A: Installation records, test results, and maintenance logs. - Q: How to maintain FTTH records?
A: Through detailed documentation and record-keeping systems. - Q: What should be documented?
A: Installation details, maintenance history, and performance data.
Future Technologies
- Q: What future FTTH technologies exist?
A: Including higher speed standards and advanced networking features. - Q: How will FTTH evolve?
A: Through increased speeds, better efficiency, and new applications. - Q: What innovations are coming?
A: Advanced multiplexing, higher bandwidths, and smart network features.
Special Applications
- Q: Can FTTH support specialized needs?
A: Yes, including medical facilities, research institutions, and data centers. - Q: What unique applications exist?
A: Remote surgery, scientific research, and real-time data processing.
Compatibility
- Q: Is FTTH backwards compatible?
A: Yes, can support existing network protocols and services. - Q: What devices work with FTTH?
A: Any network-capable device through appropriate equipment. - Q: How to ensure device compatibility?
A: Check specifications and use appropriate networking equipment.