Abstract: This paper analyzes the relevant concepts, current situation, development process and trend of the satellite mobile communication industry and the impact of Internet satellites on the industry, in order to provide reference for the author’s company to formulate a strategic development direction.
Keywords: satellite mobile communication; ground equipment manufacturing; terminal system; traditional GEO communication satellite; GEO HTS; NGSO HTS; LEO HTS

I. Industry-related concepts and current situation
(I) Relevant concepts
1. Satellite classification
Satellites can be classified into navigation, remote sensing, communication, space science, technical verification, etc.; according to orbit classification, it can be divided into geostationary orbit (GEO) satellites and non-stationary orbit satellites (medium and low orbit, elliptical orbit satellites, etc.).
2. Communication satellite classified market
At present, among the satellites in orbit, the number of communication satellites is the largest and the most widely used. Their communication applications include satellite TV live broadcast, satellite fixed communication, satellite broadcasting, satellite broadband, satellite mobile communication, etc.
In the international civil market, according to the statistics of SIA Prospective Industry Research Institute, at the end of 2021, satellite TV live broadcast, satellite fixed communication and satellite broadcasting occupied the top three markets for communication satellite applications, accounting for 77%, 13% and 6% respectively. Among them, satellite mobile communications account for a relatively small proportion, with only about 2% of the market share.
In terms of the domestic civilian market, according to the “2023-2029 China Satellite Communication Equipment Industry Market Survey Research and Investment Potential Forecast Report”, the satellite communication market scale in 2022 was 78.38 billion yuan, and the market size of mass consumer business such as satellite TV broadcasting was 63.45 billion yuan, accounting for The overall market is 81%; the market size of satellite fixed communication services is 11.65 billion yuan, accounting for 15% of the overall market; the size of the satellite mobile communication market is 3.28 billion yuan, accounting for only 4% of the overall market.
By comparing international and domestic civil market data, it can be seen that the proportion of market segments is roughly the same, among which the satellite mobile communication market is limited, accounting for only 2%-4% of the overall market.
3. The “tradition” and “new wave” of communication satellites
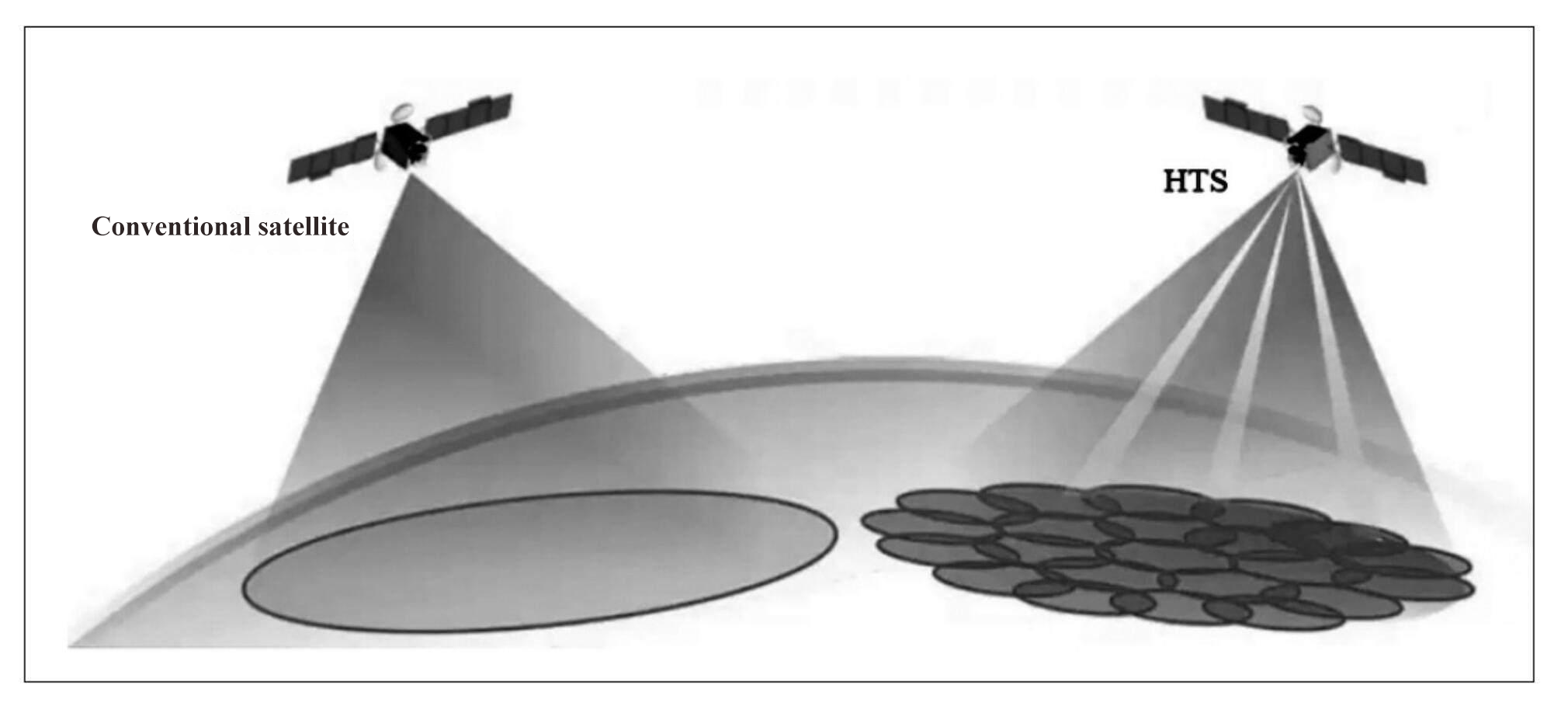
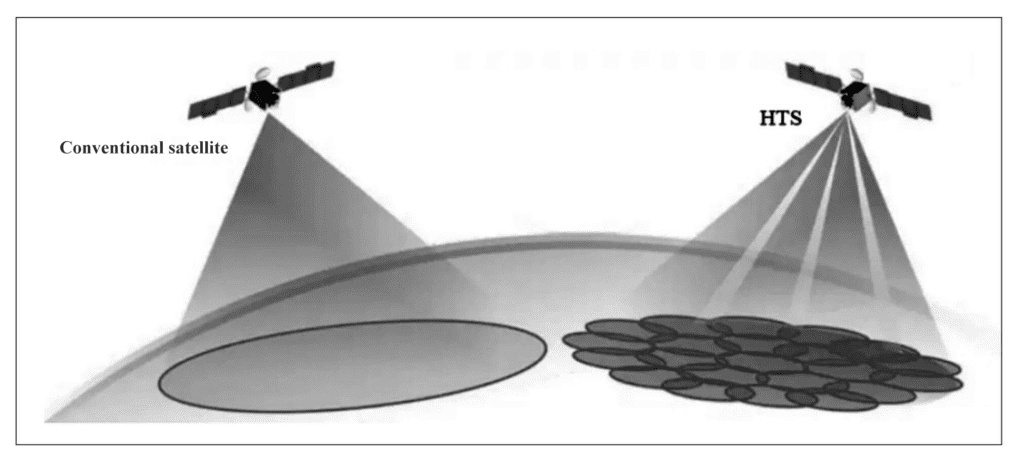
In recent years, Internet satellites have set off a “new wave” of global satellite communications, becoming an effective way to provide Internet access to land users without ground network support, air users such as civil aviation passenger aircraft, and sea users such as ocean-going ships. At the same time, it is also a new development direction of communication satellites. Internet satellite is a high-throughput satellite [1] (HTS, High Throughput Satellite). Its concept was first proposed by the Northern Sky Research Institute (NSR) of the United States and defined as “using multi-point beam and frequency multiplexing technology, in the same spectrum resources. Under the case, the communication capacity of the whole star is several times that of traditional communication satellites. [2] HTS uses a multi-beam antenna to transmit multiple beams to the earth. The adjacent beam frequency is different, and the non-adjacent beam frequency is the same, which can realize the formation of frequency multiplexing, thus greatly improving the communication capacity of the satellite. Its principle is similar to that of cellular telephone. According to the different orbits, HTS is divided into geostationary orbit high-throughput satellites (GEO HTS) and non-stationary orbit high-throughput satellites (NGSO HTS[3] or NON GEO HTS) such as mid-orbit (MEO), low orbit (LEO) and even ultra-low orbit (VLEO). The “traditional” communication satellite [4] adopts a single-feed source antenna to form a single beam with wide coverage, which cannot achieve frequency multiplexing. The bandwidth of its transponder limits the communication capacity, as shown in Figure 1. At present, satellite TV live broadcast applications, satellite broadcasting, satellite fixed communications and satellite mobile communications all use traditional communication satellites.
(II) Current situation of domestic satellite mobile communication industry
At this stage, the domestic satellite mobile communication industry has the following characteristics:
First, the industry involves the manufacturing and launch of communication satellites, the manufacturing of ground equipment and value-added services related to satellite mobile communication. Ground equipment manufacturing includes:
1. R&D and production of satellite mobile communication-related terminal equipment such as antennas, modems and amplifiers;
2 Integration of satellite mobile communication terminal systems such as dynamic and medium-pass [5], static and portable stations;
3 Ground satellite network integration and network management.
Second, the relay satellite used is a traditional GEO communication satellite. The total satellite communication capacity is about 1Gbps, and the single-link communication capacity is less than 4Mbps;
Third, the main application mode is private network communication. The application scenarios include emergency communication under various emergencies [6], blinding in remote areas of public communication networks, contagical communication, military command communication, etc.
Fourth, the main application customers are the military, public security, emergency, fire telecommunications operators and other government departments and large state-owned enterprises with the management structure of ministries and commissions-province-city (county) or group-local branches, as well as private network communication needs.
II. Industry development trend
In the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, satellite mobile communication played an irreplaceable role in emergency communication for emergency rescue and disaster relief. Since then, China’s satellite mobile communication has entered the climax of development. In the following years, many departments such as public security, fire protection, civil defense and telecommunications operators have built a huge special network covering the whole country. The use of the Internet has played a significant role in security, anti-terrorism, emergency rescue, and telecom blinding.
(I) Development trend of ground equipment
1. Autonomization of key technologies
Because the relevant key technologies were still lagging behind the international level at that time, in the private network built in China after 2008, a large number of terminal equipment such as Dongzhongtong antennas, modems and satellite amplifiers adopted Comtech, iDirect and other imported brand products. In 2010, the National Development and Reform Commission included the “satellite and satellite application industry” in the deployment of “strategic emerging industries”, which made the tack of key technologies related to satellite mobile communication ground equipment enter the fast lane and make major breakthroughs in all aspects.
In terms of dynamic antenna satellite tracking technology, the development process from satellite-based signal processing technology to inertial navigation technology has been completed, and the carrier application has also developed from on-board to on-board and airborne.
In terms of antennas, it has developed from parabolic antennas to phased array antennas. In recent years, phased array antenna products with completely independent intellectual property rights and international advanced level have emerged;
In terms of modulation and demodulation technology, many research institutions such as China Electric Science and Aerospace Science and Technology have made key technological breakthroughs and formed products with independent intellectual property rights;
In terms of amplifiers and LNB-related microwave devices, the products of many research institutions and enterprises have reached the international advanced level.
With the breakthrough of the above key technologies, the comprehensive technological competition among domestic manufacturers has become more and more fierce, and the original foreign brands have gradually withdrawn from the Chinese market.
2. Market demand for comprehensive localization substitution
In recent years, many breakthroughs in key technologies have provided technical support for the industry to achieve comprehensive localization of replacement. With the intensification of the decoupling of the Sino-US economy, during the 14th Five-Year Plan period, the trend of local substitution in the industry’s civilian market is irreversible.
(II) The development trend of satellites
The emergence of high-throughput satellites (HTS) has greatly improved the disadvantages of traditional communication satellites in terms of communication capacity, bandwidth and cost, and has once again ignited human enthusiasm and hope for broadband satellites [7].
1. The current situation and development trend of HTS abroad
In terms of GEO-HTS, in 2005, IPSTAR-1, the world’s first GEO-HTS, was successfully launched, with a communication capacity of 45Gbps and a communication rate of 4Mbps. Since then, 26 satellite operators around the world, including ViaSat and Hughes, have operated dozens of GEO HTS. After 2010, the communication capacity and speed of GEO HTS have been rapidly improved, with the capacity increasing to 300Gbps and the speed reaching 50Mbps. On May 1, 2023, the transmitted ViaSat-3 has a communication capacity of 1Tbps and a communication rate of 100Mbps.
In terms of NGSO HTS, the Starlink constellation has become a global hot spot. The constellation includes about 12,000 satellites, which are divided into two categories: low orbit (LEO) and ultra-low orbit (VLEO). LEO satellite works in the Ku and Ka frequency bands, with 247 receiving and 275 transmitting channels with a channel bandwidth of 50MHz; VLEO satellite operating in the V frequency band, with 140 receiving and 240 transmitting channels, service channel bandwidth of 1000MHz and measurement and control channel bandwidth of 10MHz. As of March 18, 2023, a total of 4,105 Starlink satellites were launched, 3,803 in orbit, and more than 1 million Internet access users. In addition to Starlink constellations, nearly ten NGSO HTS constellations such as O3b and OneWed are being deployed or planned to be deployed.
Due to the serious privatization of land in foreign countries, the laying of ground optical cables and the location of communication base stations have been greatly hindered. There are many land areas that are not covered by the ground network. Some areas realize backbone network communication and Internet access through traditional GEO communication satellites, but their communication capacity, speed and cost and optical fiber network. There is a big difference between them, and the emergence of HTS effectively makes up for these gaps. Therefore, the application of foreign HTS has a huge land application market, and the application demand of offshore ships and airline aircraft is also very considerable.
2. Current situation and development trend of domestic HTS
In terms of GEO HTS, China has launched four GEO HTS such as Asia-Pacific 6D, Zhongxing 16, 19 and 26, and will launch GEO HTS such as Zhongxing 27 in the future. The total communication capacity is planned to exceed 400Gbps. In July 2020, Zhongxing 16 realized the Internet access application of 150Mbps on civil airliners, providing passengers with an air Internet experience with 4G effect. Since the first flight, there have been a total of 1,784 service flights, providing Internet services for nearly 20,000 passengers.
In terms of NGSO HTS, in April 2021, China established China Satellite Network Group Co., Ltd. and submitted to ITU the spectrum application for the two low-orbit constellations of GW-A59 and GW-2, with a total of 12,992 satellites.
Compared with foreign countries, the domestic terrestrial network is quite developed. According to the “Economic Operation of the Communications Industry of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology in 2022” and other reports, by the end of 2022, the total length of China’s optical cable lines has reached 59.58 million kilometers (the first in the world), and the optical fiber entry ports have reached 1.071 billion; the broadband rate of administrative villages and poverty alleviation villages has reached 100%, and the administrative The proportion of village optical fiber and 4G is more than 99%. With such a developed terrestrial network, the land Internet access market for domestic HTS is very limited, and the maritime and air markets will also face fierce international competition. Therefore, the market prospect of domestic HTS Internet access applications is not very clear.
3. HTS business operation model
The commercial operation mode of the satellite is divided into two modes: open mode and closed mode.
In open mode, satellite operators only sell or rent satellite transponder bandwidth, customers configure terminal equipment, integrate terminal systems, and build independent satellite communication networks (HTS application customers need to configure their own Xinguan stations); in closed mode, satellite operators or their distributors operate satellites and build xinguan stations. And sell terminal equipment and services of unified communication system and protocol to users.
The established satellite communication network in China adopts traditional GEO satellite communication, so there is no need to close the station, and all of them are set as open operation mode. In this case, each user can use terminal equipment with different systems and protocols, which finally forms the scene of “hundreds of countries” in the domestic satellite ground equipment manufacturing industry. HTS adopts multi-point beam and frequency multiplexing technology, and communication can only be carried out through the signal station. Both modes can be used.
Most of the closed-operated HTS networks abroad adopt asymmetrical design (receiving bandwidth is greater than the upload bandwidth), which is suitable for Internet access, such as ViaSat’s ViaSat 1-3 satellites, SpaceX’s Starlink constellation, etc.; open operation of HTS networks are mostly adopted and The same symmetrical design as traditional satellites (the upstream and downstream bandwidth is consistent) is suitable for satellite mobile communications, such as Intelsat’s Epic satellite, SES’s SES12-15 satellite, etc. That is to say, the business operation model adopted depends on the ultimate target market of HTS. Domestic satellite operators have piloted the closed operation mode in the applications of Zhongxing 16 and Zhongxing 26, and the operating units have unified deployment of ground business systems and application platforms. However, the author believes that domestic satellite operators do not have the R&D and production capacity of relevant terminal equipment, and also need the support of many domestic equipment manufacturers. Under the closed operation mode, the profit margin of equipment manufacturers is low and the willingness to participate is low, which is not conducive to the market promotion of HTS satellite applications, and is not conducive to market competition and technology. The development of art. The open operation mode is suitable for satellite mobile communication, and the willingness of domestic manufacturers is high, which is more conducive to the promotion and technological progress of the HTS satellite application market.
III. Concluding remarks
The domestic satellite mobile communication industry is moving towards rapid development, and the national production trend of satellite communication-related equipment and devices is becoming more and more obvious. Although the current market demand and operating mode of high-throughput satellites (including GEO-HTS and NGSO HTS) are not very clear, the trend of high-throughput communication satellites gradually replacing traditional communication satellites in the future cannot be reversed, which will greatly change the industrial pattern of the satellite mobile communication industry. Therefore, relevant manufacturers and research institutions in the domestic satellite mobile communication industry will face greater opportunities and challenges.