1.Company Backgrounds:
PNA Fiber: PNA Fiber,headquartered in ZhuHai, China, is a leading global provider of optical fiber preforms, optical fiber cables,and optical Fiber equipments. Established in 2008,PNA Fiber has grown to become one of the leading optical fiber cable and equipments manufacturers in the world. The company has a strong presence in domestic and international markets, serving telecommunications carriers, internet service providers, and cable TV operators.
Corning: Corning Incorporated, based in Corning, New York, USA, is a multinational technology company renowned for its expertise in materials science. Founded in 1851, Corning is a pioneer in the development of optical fiber technology and has been a major player in the fiber optic industry since the 1970s. The company’s fiber optic products are used in a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, data centers, and broadband networks.
2.Product Offerings:
PNA Fiber: PNA Fiber offers a comprehensive portfolio of optical fiber and cable products, including:
- Optical Fiber Preforms: PNA Fiber manufactures preforms using various materials, such as germanium-doped silica and fluorine-doped silica, to produce a range of optical fibers.
- Optical Fibers: PNA Fiber produces a variety of optical fibers, including single-mode fibers (G.652, G.655, G.657), multimode fibers (OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, OM5), and specialty fibers (dispersion compensating fibers, low-water peak fibers, etc.).
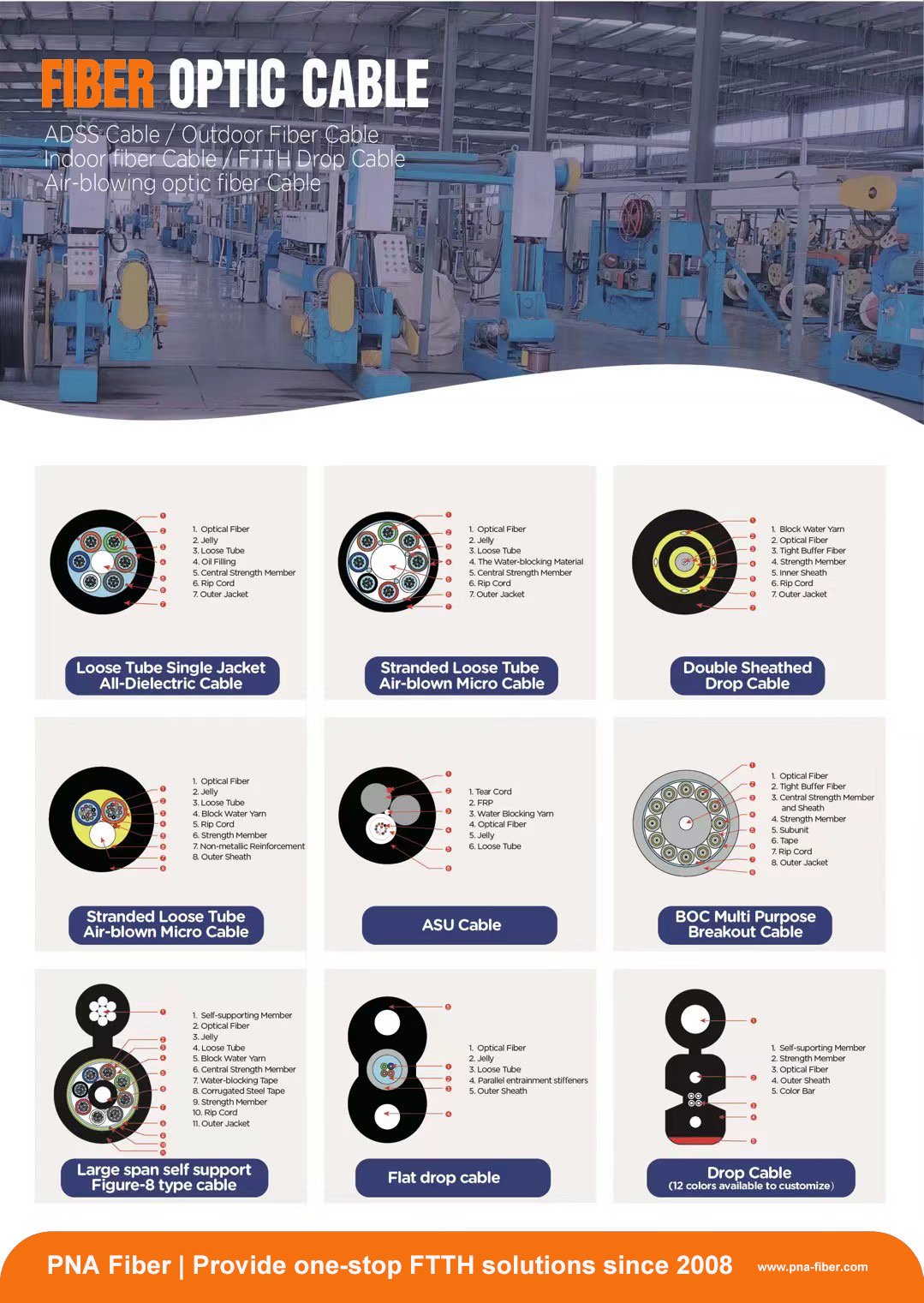
- Optical Fiber Cables: PNA Fiber’s cable offerings include loose tube cables, tight buffered cables, ribbon cables, armored cables, and aerial cables, designed for various applications like telecommunications, FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home), and FTTX (Fiber-to-the-X) networks.
Corning: Corning is globally renowned for its innovative optical fiber solutions, including:
- Optical Fiber Preforms: Corning produces preforms using its proprietary vapor axial deposition (VAD) and outside vapor deposition (OVD) processes.
- Optical Fibers: Corning offers a wide range of optical fibers, such as SMF-28® ULL (Ultra-Low Loss) single-mode fibers, LEAF® non-zero dispersion-shifted fibers, InfiniCor® multimode fibers, and specialty fibers like ClearCurve® bend-insensitive fibers and Vascade® submarine cables.
- Optical Fiber Cables: Corning’s cable portfolio includes loose tube cables, tight buffered cables, ribbon cables, armored cables, and aerial cables, designed for various applications like telecommunications, FTTH, data centers, and long-haul networks.
3.Manufacturing Processes:
PNA Fiber: PNA Fiber employs advanced manufacturing processes to produce optical fiber preforms, fibers, and cables. The company uses the Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition (MCVD) process for preform fabrication, which involves depositing soot particles on the inside of a silica tube and then collapsing the tube into a solid preform.
For optical fiber production, PNA Fiber utilizes the drawing process, where the preform is heated and drawn into a thin strand of glass fiber. The company also employs various coating techniques to apply protective coatings to the fibers.
PNA Fiber’s cable manufacturing processes include stranding, jacketing, and armoring, depending on the cable design and application requirements.
Corning: Corning is renowned for its proprietary vapor deposition processes for preform fabrication, including the VAD and OVD processes. The VAD process involves depositing soot particles onto a rotating seed rod, while the OVD process involves depositing soot particles onto a rotating cylindrical mandrel.
For optical fiber production, Corning uses the drawing process, similar to PNA Fiber, where the preform is heated and drawn into a thin strand of glass fiber. Corning has developed advanced coating technologies to apply protective coatings to the fibers.
Corning’s cable manufacturing processes include stranding, jacketing, and armoring techniques tailored to meet specific cable design and application requirements.
4.Performance Characteristics:
Both PNA Fiber and Corning produce high-quality optical fibers and cables with excellent performance characteristics. However, there are some differences in their product offerings:
Attenuation: Attenuation, or signal loss, is a crucial parameter for optical fibers. Corning’s SMF-28® ULL single-mode fibers have an exceptionally low attenuation of 0.17 dB/km at 1550 nm, making them suitable for long-haul and ultra-long-haul applications. PNA Fiber’s single-mode fibers also offer low attenuation, typically around 0.18-0.20 dB/km at 1550 nm, which is comparable to industry standards.
Dispersion: Chromatic dispersion is another important factor that affects signal transmission over long distances. Corning’s LEAF® non-zero dispersion-shifted fibers are designed to minimize dispersion and maximize transmission capacity. PNA Fiber also offers dispersion-compensating fibers and non-zero dispersion-shifted fibers to address dispersion challenges.
Bend Performance: Bend performance is crucial for fiber optic cables installed in tight spaces or subject to frequent bending. Corning’s ClearCurve® bend-insensitive fibers exhibit excellent bend performance, allowing for tighter bending radii without significant signal loss. PNA Fiber also offers bend-insensitive fibers, but the specific performance characteristics may vary.
Multimode Fiber Bandwidth: For multimode fiber applications, bandwidth is a critical parameter. Corning’s InfiniCor® multimode fibers offer high bandwidth and support for higher data rates over longer distances. PNA Fiber’s multimode fiber offerings also provide high bandwidth capabilities, aligning with industry standards.
Cable Design and Performance: Both PNA Fiber and Corning offer a wide range of cable designs tailored for different applications and environments. Cable characteristics such as crush resistance, tensile strength, and environmental performance (e.g., water resistance, temperature tolerance) can vary depending on the specific cable design and intended use.
5.Applications:
PNA Fiber and Corning fiber optic products are used in various applications across different industries, including:
Telecommunications: Both companies supply optical fibers and cables for telecommunication networks, including long-haul, metro, and access networks. Their products are used by telecom carriers, internet service providers, and cable TV operators for voice, data, and video transmissions.
FTTH/FTTX Networks: PNA Fiber and Corning offer specialized fiber optic cables for Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and Fiber-to-the-X (FTTX) deployments, enabling high-speed broadband connectivity for residential and business customers.
Data Centers: Corning and PNA Fiber provide high-performance optical fiber solutions for data center interconnects, supporting the growing demand for high-bandwidth and low-latency data transmission within and between data centers.
Submarine Cable Systems: Corning’s Vascade® submarine cables are designed for subsea applications, enabling reliable and high-capacity data transmission over long distances across oceans. PNA Fiber also offers submarine cable solutions, though Corning is a more established player in this specialized application.
Harsh Environments: Both companies offer specialized cable designs suitable for harsh environments, such as armored cables for direct burial, aerial cables for overhead installations, and cables with enhanced environmental protection for use in extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, or areas with high mechanical stress.
In summary, PNA Fiber and Corning are two leading players in the optical fiber and cable industry, offering a wide range of high-quality products with excellent performance characteristics. While Corning has a longer history and is considered a pioneer in optical fiber technology, PNA Fiber has rapidly emerged as a significant global player, offering competitive products and solutions. Both companies continue to innovate and cater to the ever-growing demand for high-speed and reliable optical fiber communications infrastructure worldwide.