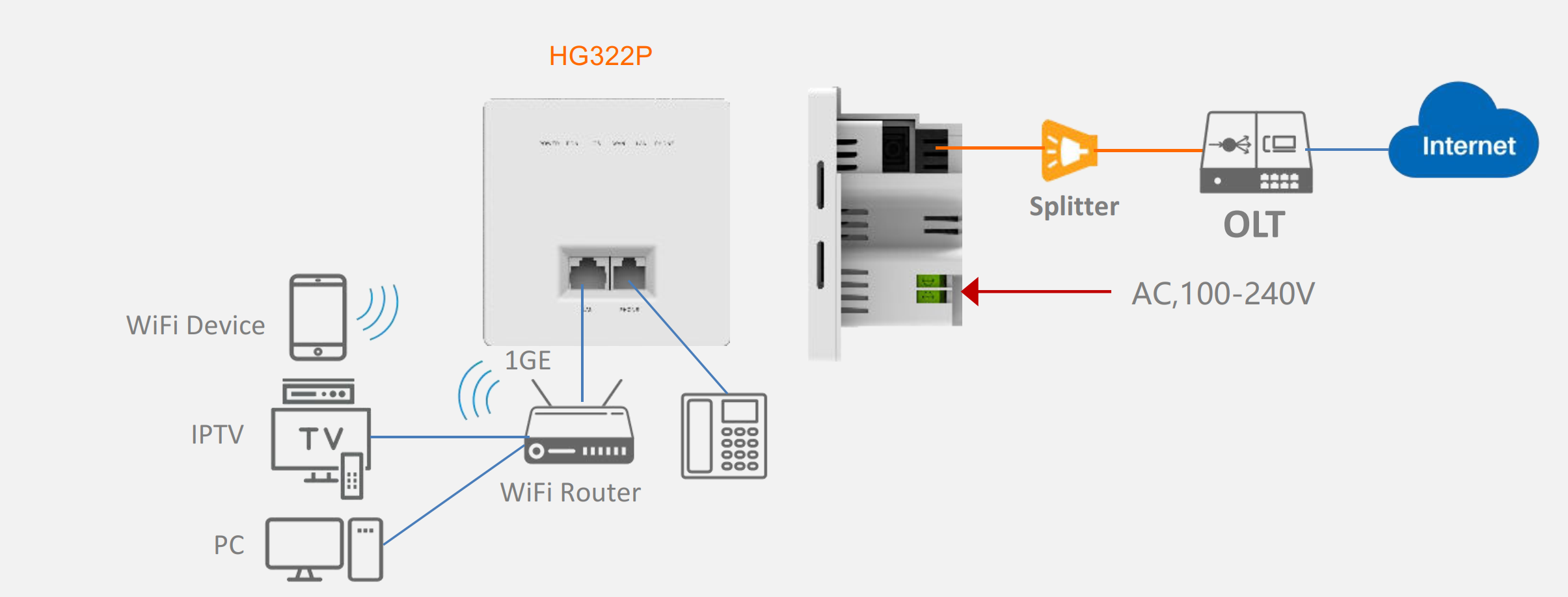
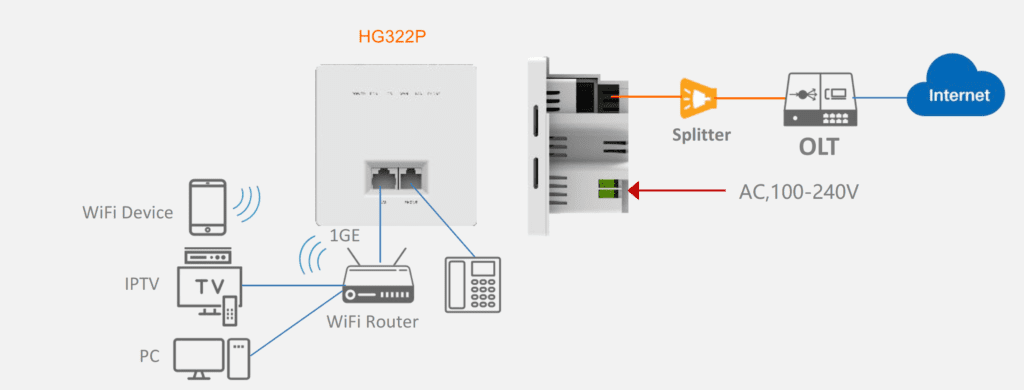
XPON (X Passive Optical Network) is a term used to describe various types of passive optical network (PON) technologies, including GPON, EPON, and the more recent standards like XGS-PON and NG-PON2. The “X” in XPON is a variable that can represent different PON standards.

Dual-mode technology, in the context of XPON, refers to the ability of a single network element or system to support multiple PON standards simultaneously. This flexibility allows service providers to deploy and leverage different PON technologies within the same network infrastructure, enabling a smoother transition between generations of PON technologies and maximizing the return on investment (ROI) from existing network assets.
- XPON Dual-Mode Technology: The XPON dual-mode technology typically involves the use of dual-mode optical line terminals (OLTs) and dual-mode optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs). These network elements are designed to support both legacy PON standards (e.g., GPON) and newer PON standards (e.g., XGS-PON or NG-PON2) concurrently. For example, a dual-mode OLT can have separate line cards or ports dedicated to different PON technologies, allowing it to serve both GPON and XGS-PON subscribers simultaneously. Similarly, a dual-mode ONU or ONT can communicate with both GPON and XGS-PON OLTs, enabling a seamless transition between the two technologies without the need for immediate replacement of customer premises equipment (CPE).
- Benefits of XPON Dual-Mode Technology: a. Smooth Migration Path: Dual-mode technology allows service providers to migrate from legacy PON technologies to newer, higher-speed PON standards gradually, without disrupting existing services or requiring immediate replacement of all network elements. b. Investment Protection: By leveraging dual-mode capabilities, service providers can extend the lifespan of their existing PON infrastructure and maximize the ROI from previous investments, reducing the overall cost of network upgrades. c. Increased Flexibility: Dual-mode networks offer greater flexibility in terms of service offerings and bandwidth allocation, enabling service providers to cater to diverse customer needs and deliver differentiated services based on specific requirements. d. Scalability: Dual-mode OLTs and ONUs provide a scalable solution, allowing service providers to incrementally add capacity and subscribers as their network demands grow, without the need for a complete infrastructure overhaul.
- XPON Dual-Mode Products: Several network equipment manufacturers offer XPON dual-mode products to support service providers in their transition to newer PON technologies. Some examples include:
- a. Dual-Mode OLTs: Companies like Huawei, ZTE, Nokia, and Fiberhome offer dual-mode OLTs that can support both legacy PON standards (e.g., GPON) and newer standards (e.g., XGS-PON, NG-PON2) simultaneously.
- b. Dual-Mode ONUs/ONTs: Manufacturers like Huawei, ZTE, Technicolor, and Alphion provide dual-mode ONUs or ONTs that can interoperate with different PON technologies, enabling a smooth upgrade path for service providers.
- c. Dual-Mode Residential Gateways: Companies like Zyxel, Huawei, and ZTE offer dual-mode residential gateways that combine the functionality of an ONU/ONT with a home router, enabling service providers to deliver both data and voice services over PON networks.
- Market for XPON Dual-Mode Products: The market for XPON dual-mode products is driven by the global demand for high-speed broadband services and the need for service providers to upgrade their existing PON infrastructure to support higher bandwidths and advanced applications. According to a report by Dell’Oro Group, the global PON equipment market, including OLTs, ONUs/ONTs, and residential gateways, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 10% between 2021 and 2026, driven by the adoption of XGS-PON and NG-PON2 technologies. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, is currently the largest market for XPON dual-mode products, as service providers in the region are actively deploying and upgrading their PON networks to meet the growing demand for high-speed internet and support various initiatives like smart cities and 5G deployments. North America and Europe are also significant markets for XPON dual-mode products, as service providers in these regions are investing in fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) deployments and upgrading their existing PON networks to support higher bandwidths and advanced services. Overall, the market for XPON dual-mode products is expected to continue growing, driven by the increasing demand for high-speed broadband services, the need for network upgrades, and the desire of service providers to maximize their existing investments while ensuring a smooth transition to newer PON technologies.
- Key Players and Competitive Landscape:The market for XPON dual-mode products is highly competitive, with several major players vying for market share. Some of the key players in this space include:
- a. Huawei: As a leading provider of telecommunications equipment, Huawei has a strong presence in the XPON dual-mode market. The company offers a range of dual-mode OLTs, ONUs/ONTs, and residential gateways that support both legacy and next-generation PON standards.
- b. ZTE: ZTE is another prominent player in the XPON dual-mode market, offering a comprehensive portfolio of dual-mode OLTs, ONUs/ONTs, and residential gateways. The company is particularly strong in the Asia-Pacific region and has a significant market share in China.
- c. Nokia: With its acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent, Nokia has become a major player in the PON market, including XPON dual-mode products. The company offers dual-mode OLTs and ONUs/ONTs, leveraging its expertise in fiber optic networks.
- d. Fiberhome: Based in China, Fiberhome is a leading provider of XPON dual-mode products, particularly in its domestic market. The company offers a range of dual-mode OLTs, ONUs/ONTs, and residential gateways that support various PON standards.
- e. Alphion: Alphion is a prominent supplier of ONUs/ONTs, including dual-mode products that support GPON, XGS-PON, and NG-PON2 standards. The company has a strong presence in the Asia-Pacific region and is expanding its global reach.
- f. Technicolor: Formerly known as Technicolor Connected Home, this company is a major provider of residential gateways, including dual-mode products that support various PON standards.
- These key players, along with several other companies, are continuously investing in research and development to enhance their XPON dual-mode product offerings and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving market.
- Challenges and Future Developments:While the XPON dual-mode technology offers numerous benefits, it also presents some challenges that need to be addressed:
- a. Interoperability: Ensuring seamless interoperability between different vendors’ XPON dual-mode products can be a challenge, as various manufacturers may implement proprietary features or interpretations of PON standards. Standardization efforts and multi-vendor testing are crucial to address this issue.
- b. Power Consumption: As XPON dual-mode products support multiple PON standards simultaneously, they may consume more power than their single-mode counterparts. Efforts are underway to develop more energy-efficient XPON dual-mode solutions to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
- c. Cost and Pricing: While XPON dual-mode products offer investment protection and a smooth migration path, their initial cost can be higher compared to single-mode PON equipment. Service providers need to carefully evaluate the long-term benefits and ROI when adopting XPON dual-mode solutions.
- d. Training and Support: Deploying and managing XPON dual-mode networks may require specialized training and support for service provider personnel, as they need to be familiar with multiple PON standards and their specific configurations and operational aspects.
- Looking ahead, the XPON dual-mode technology is expected to evolve further, with the development of new PON standards and the integration of advanced features such as software-defined networking (SDN), network virtualization, and intelligent traffic management. Additionally, the convergence of PON and 5G technologies is an area of active research and development, aiming to leverage the high-speed and low-latency capabilities of next-generation PON networks for 5G backhaul and fronthaul applications.