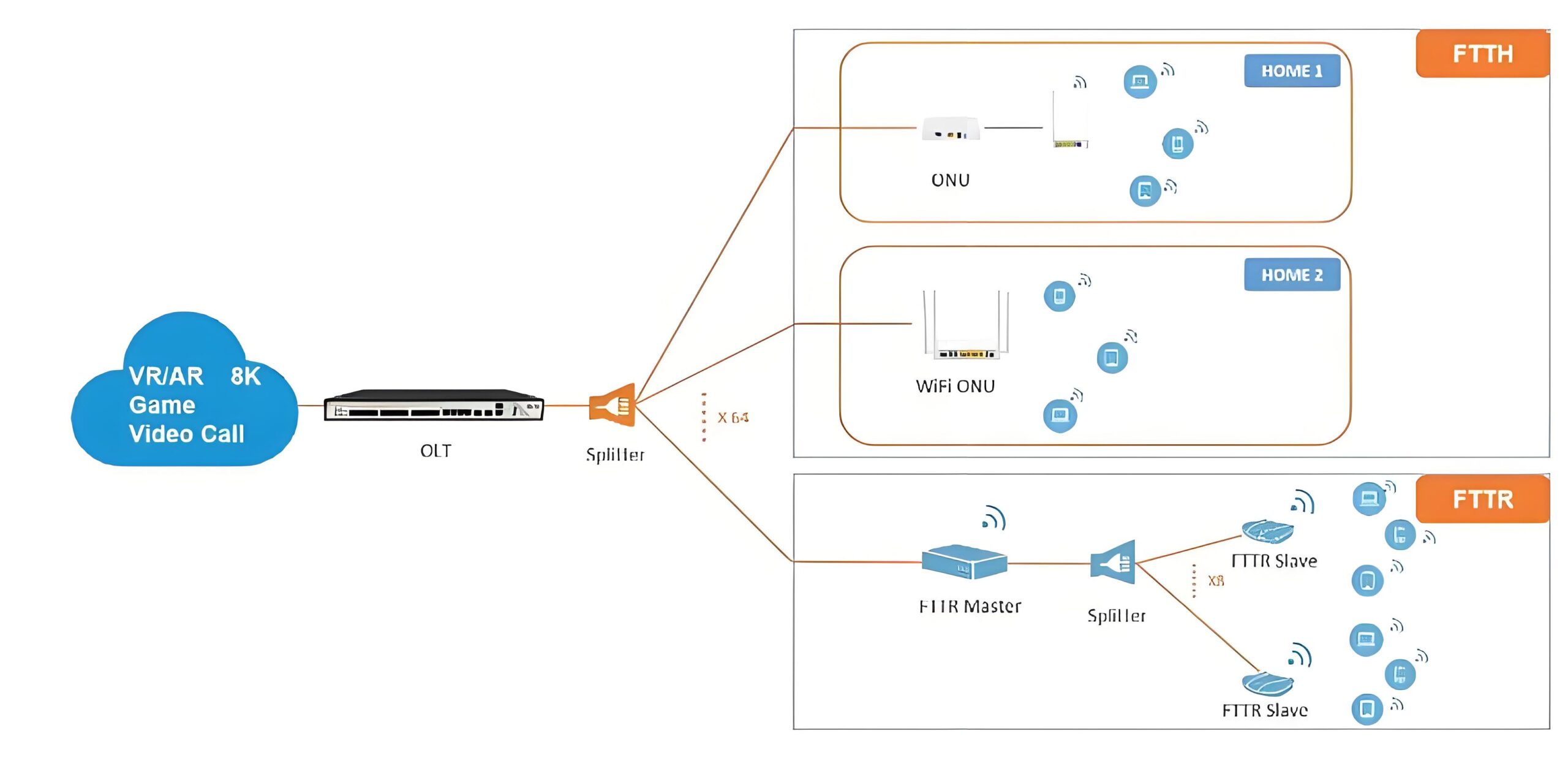
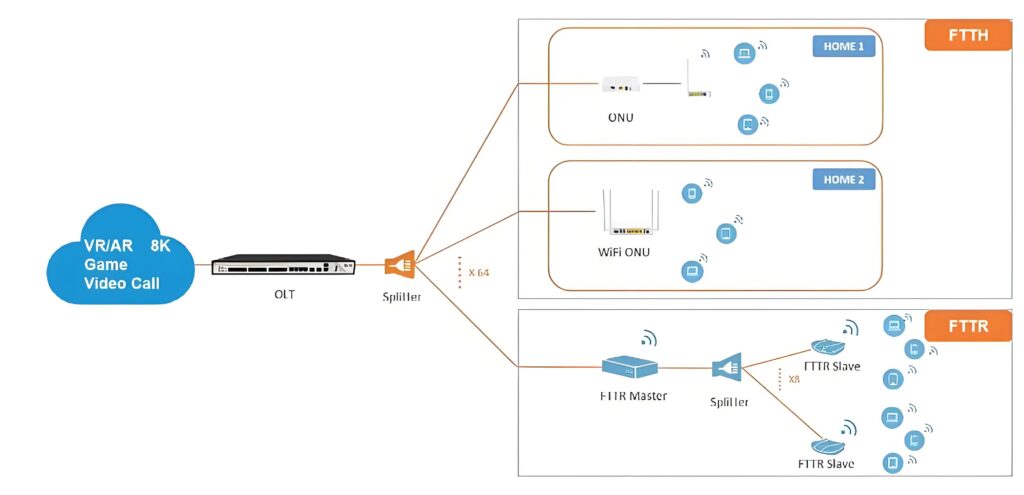
What is FTTR?
FTTR is a new coverage mode of home network in the Gigabit era. It is based on FTTB (ten-Gigabit era optical fiber to building) and FTTH (100 Gigabit era optical fiber to household), and then further derives the optical fiber deployment to every room, so that every room can reach the Gigabit optical fiber network speed and realize the whole house W A new networking scheme with Wi-Fi 6 Gigabit full coverage.

Why do you need FTTR?
In the post-epidemic era, a family can study at home, work from home, and live at home through the same time. With the increasing price of network demand, problems such as poor WIFI coverage, video jamming, and slow network speed have become common problems. In addition, with the poor quality of network cables, the increase in construction area and the rapid development of new interconnected applications of cloud VR, high-definition TV and smart homes, urban residents have also put forward higher requirements for the quality of home networks.
What are the advantages of FTTR?
The traditional networking scheme uses a single light cat and router. The network cable only goes to the weak electric box and the living room. The Wi-Fi coverage area is limited, and the transmission rate of the network cable is limited, which cannot meet the bandwidth demand. In addition, after passing through the wall, the signal and network speed are seriously attenuated, and the Wi-Fi high-speed network coverage of the whole family cannot be achieved.
The FTTR whole house intelligent Gigabit optical fiber adopts the mode of 10 Gigabit optical cat 1 tow N. Whether in the corridor or into the room, all optical fiber is connected. The transmission capacity is strong, the transmission rate is higher, and the network cable life is longer. It can support 10 Gigabit uplink and dynamically display the wide technical signal. The ability through the wall is stronger, which reduces the signal attenuation. Enable optical fiber to be laid in every room, realizing real whole-house Wi-Fi6, Gigabit blind-free coverage, so that everyone in the family can enjoy the best Internet experience brought by Gigabit light bands in every place at home.
In addition to the advantages of fast Gigabit optical fiber network speed and no dead corner coverage of the whole house, it can also support 256 terminal device connections, which is 8 times the maximum number of connections of the traditional network (the maximum number of connections of the traditional network is 8-10), which can effectively ensure the whole house intelligence of home computers, TV, mobile phones, tablets, VR and so on. Terminal network use. In addition, in the traditional wiring process, the problem of unsightly wiring can also be easily avoided after updating to FTTR whole house gigabit optical fiber. It is compatible with obvious dark line networking, and the line is more beautiful, does not destroy the decoration style, and integrates with the home environment. At the same time, FTTR gigabit optical fiber, especially suitable for 100 square meters. Large flats above meters, villas and other types of apartments.
Does FTTR really mean higher network speed?
In the publicity of many operators, it is mentioned that FTTR can provide higher network rates, which is theoretically correct. Because optical fiber can easily achieve kilometer-level network transmission, and the network bandwidth loss in transmission is basically negligible. At the same time, optical fiber can indeed carry larger network bandwidth, and the 100G-level network in the data center basically relies on optical fiber transmission. The “copper core network cable” will cause great losses with the increase of transmission distance. Therefore, network cables are indeed not as good as optical fiber in long-distance transmission and large-bandwidth transmission.
But if we combine the actual use scenarios of the home network, the advantages of optical fiber are actually not much.
According to the specification definition of the network cable, we can find that the super six types of network cable can achieve 10 gigabits (10Gbps) transmission at a distance of 100m. In addition, six types and super five types of network cables are not unable to run 100 megabytes. For example, if you want to run 10,000 megabytes, the limit distance of a single network cable is about 90m. The limit distance of the super five types of network cable running full of 10 megabytes is about 55m. ( The quality of network cables of the same specifications of different brands is slightly different. The above data is for reference only)
Does FTTR really mean better network coverage?
In the publicity of many operators, it is mentioned that FTTR can provide better network coverage. In short, there are “signals everywhere and the signals are full” at home.
At present, the network configuration of many homes is actually a light cat + a wireless router. The wireless signal sent by the wireless router will be significantly reduced after passing through the wall. Therefore, the WiFi signal in the room where the wireless router is located is often very good, but the WiFi signal in other rooms will be worse, and some rooms far away will not even have WiFi signal.
FTTR uses a main light cat and multiple slave light cats for indoor WiFi coverage. From the light cat is deployed to each room, the main light cat and the slave cat are connected by optical fiber. This networking method can be roughly understood as a wireless router in each room, so that the signal in each room is naturally full.
However, this networking method of deploying multiple wireless transmitting points is not a “patent” of FTTR, and “AC+AP” and Mesh networking can also achieve good network coverage.
AC+AP: AC is an access controller, and AP is a wireless access point. AC uniformly manages each AP and provides network to users through APs deployed in different rooms.
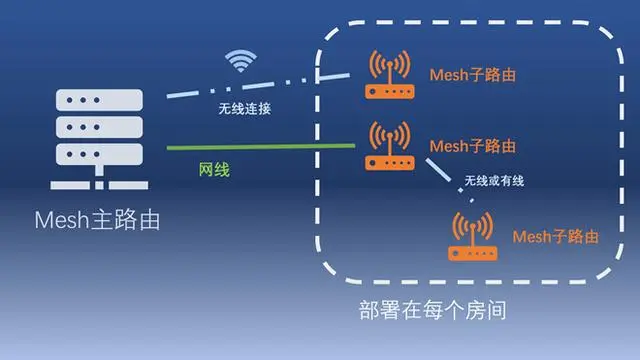
Mesh network: Mesh includes a main route (master node) directly connected to the optical cat, and one or more sub-routes (child nodes). The main route (master node) and the subroute (child node) can be connected by wireless/wired/wired + wireless hybrid. Because each node can be wirelessly connected, it can be used even if there is no embedded network cable during decoration, and the deployment is more flexible.
Both Mesh networking and AC+AP can achieve full house coverage of wireless network and full roaming (walking back and forth in different rooms, and WiFi connection can be seamlessly switched). Therefore, FTTR has no obvious advantage in network coverage compared with Mesh networking or AC+AP, and the advantage of FTTR mentioned in the publicity in network coverage is only relative to a single wireless router.


Who is FTTR suitable for?
FTTR is undoubtedly technologically advanced, but if combined with the actual situation of the current home network, many advantages are not used at all, and even become disadvantages. For example:
1. Optical fiber long-distance transmission is loss-free, but the home network does not need long-distance transmission at all. The distance between the two nodes (such as the router and the computer) is more than ten meters away. In the case of short distances, the transmission loss of the network cable is negligible.
2. The maximum transmission bandwidth of optical fiber is much larger than that of network cable. The 100G (100,000 Gigabit) network of the data center is basically transmitted through optical fiber. But the 100G network has little to do with the “home network”. At present, the “home network” provided by operators is only a few gigabytes, and some digital enthusiasts will build a 10G (ten thousand megabytes) intranet at home. However, for networks below 10G, optical fiber has no advantage, and the network cable is enough.
3. The actual experience brought by the high-speed network is small. China Mobile mentioned earlier that 2000M broadband can download a 2GB movie in 8 seconds. Then calculate according to this data, download a 2GB movie with 1000M broadband, and it can be done in 16 seconds. 500M broadband download 1 2GB movie, it can be done in 32 seconds. 32 seconds is still acceptable for users, and the cost of 500M broadband is much cheaper than 2000M broadband. Moreover, the above data is only theoretical data. In the actual download process, the download speed will be largely limited by the website where the download resource is located. For example, the download speed of a network disk for non-members is limited to 100kB/s. So even if you have 1000M broadband, if you don’t have a member, the download speed can only reach 100kB/s. In addition to this “human restrictions”, there are other restrictions due to objective conditions such as website software and hardware. For example, when you use 1000M broadband to download a resource, the download speed is 50MB/s on average (about 400M broadband speed). In this case, if you upgrade to 2000M broadband to download the same resource, the speed is still only 50MB/s. The slow download speed is sometimes a problem of the resource itself, not the network.
Powered By EmbedPress
4. Optical fiber is much more fragile than network cable, and the corresponding connector is more troublesome to make. The internal core of the optical fiber is actually very fragile, and it will basically be scrapped when it is bent to a right angle. Therefore, many optical fibers will wrap some steel wire on the outer skin to protect the core. Some home fibers deployed may even be scraped by pets. In addition, the production of optical fiber connectors, whether cold or hot melt, is much more complicated than network cable connectors, and the corresponding production tools are more expensive.
The above reasons are actually the reason why many technical people are not optimistic about FTTR. After all, the advantages are not obvious, and they need to pay more money. However, if you look at FTTR as a networking service, it may be quite affordable.
For those who know technology and like to toss, it is often more appropriate to buy their own equipment to set up AC+AP or Mesh. But for those who don’t know much about technology or don’t like tossing, if there are still high requirements for the network, they can only choose to find a company design plan that provides networking services and buy the corresponding equipment from these companies. In fact, the cost of such a set is not small.
The FTTR provided by the operator is actually not too expensive from the perspective of “networking service”. After all, the operator package design, equipment, installation, and after-sales service is also very guaranteed. Therefore, for those who don’t know much about technology or don’t like tossing, FTTR is actually quite suitable.
Pre-embedded optical fiber or network cable?
For those who know technology and like to toss, embedded optical fiber or network cable is indeed a matter of consideration.
In this regard, if the network you expect to use in the next few years is below 10 gigabits (10G), then pre-embed the network cable. If it is more than 10 million gigabytes, the optical fiber will be embedded.
In addition, if it is still in the decoration stage, it is recommended to bury the pipeline. In this way, whether you use optical fiber or network cable in the future, you can penetrate flexibly.
When pre-burying the line pipe, try not to use the right-angle elbow as shown in the figure above. This kind of elbow threading machine can’t be penetrated. It will be very troublesome if you want to use the threading machine to thread it in the future.
If the embedded pipe needs to be turned, a large arc elbow or a spring bender (provided that the pipe supports cold bending) can be used to bend the pipe, which are “friendly” to the threader.