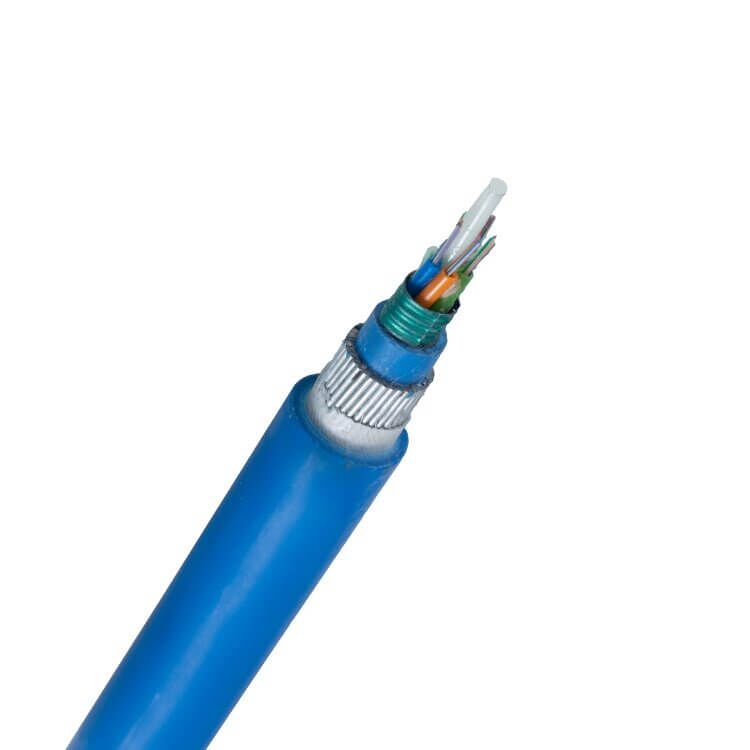
In today’s increasingly connected world, the demand for high-speed and reliable internet connectivity is on the rise. Fiber optic technology has emerged as the frontrunner in meeting these demands, with fiber optic patch cables playing a crucial role in establishing seamless connections. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a detailed understanding of fiber optic patch cables, their types, uses, and benefits. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of fiber optic patch cables!


1. What are Fiber Optic Patch Cables?
Fiber optic patch cables, also known as fiber jumper cables or fiber optic patch cords, are essential components in fiber optic communication systems. They provide a reliable and flexible means of connecting various devices, such as switches, routers, and servers, to transmit data via fiber optic cables.
2. Types of Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
a. Single-Mode Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
Single-mode fiber optic patch cables are designed to transmit data over longer distances with higher bandwidth. They use a narrow core, typically 9 microns in diameter, allowing for a single transmission mode. These cables are commonly used in long-haul telecommunications, high-speed internet connections, and backbone networks.
b. Multi-Mode Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
Multi-mode fiber optic patch cables have a larger core diameter, usually 50 or 62.5 microns, enabling multiple transmission modes. They are suitable for shorter distances, such as within buildings or local networks. Multi-mode cables are widely used in LANs, CCTV systems, and data centers.
3. Construction of Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
Fiber optic patch cables consist of several key components that work together to ensure efficient data transmission:
a. Fiber Optic Connectors:
Connectors are attached to both ends of the fiber optic patch cable, enabling easy and secure connections with other devices. Common connector types include SC, LC, ST, and MTP/MPO.
b. Fiber Strands:
The fiber strands, made of glass or plastic, are the core components that transmit light signals. Single-mode cables have a single strand, while multi-mode cables have multiple strands.
c. Outer Jacket:
The outer jacket protects the fiber strands from external factors such as moisture, dust, and
physical damage. It is usually made of PVC or LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) materials to ensure fire safety.
d. Strength Members:
Strength members, typically made of Kevlar or fiberglass, provide additional reinforcement and protect the delicate fiber strands from stretching or breaking.
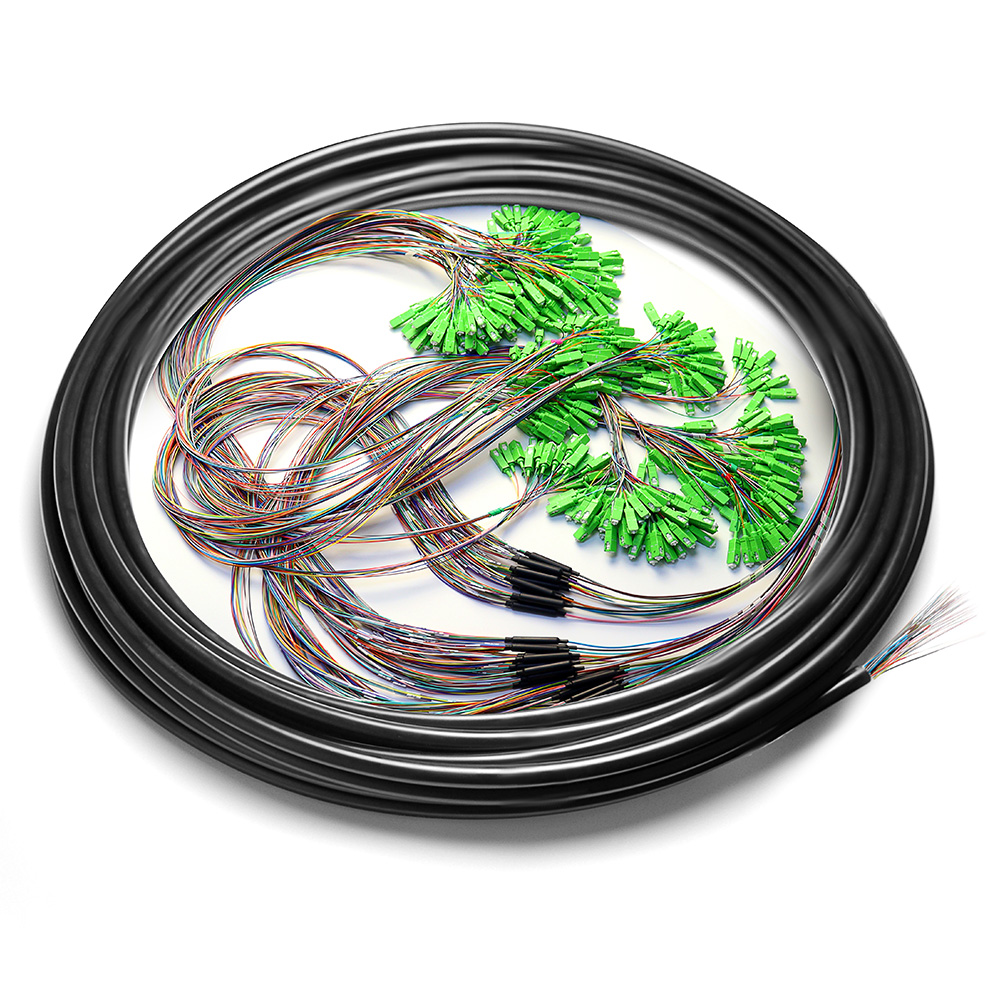


4. Benefits of Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
a. High Bandwidth and Speed:
Fiber optic patch cables offer significantly higher bandwidth and faster data transmission speeds compared to traditional copper cables. They can support data rates of up to 100 Gbps and beyond, ensuring seamless streaming, downloading, and uploading experiences.
b. Low Signal Loss and Interference:
Due to the use of light signals instead of electrical signals, fiber optic patch cables experience minimal signal loss and interference. This results in clearer and more reliable data transfers, even over long distances.
c. Long Transmission Distances:
Fiber optic patch cables can transmit data over much longer distances compared to copper cables. Single-mode cables can reach distances of up to 10 kilometers without the need for signal regeneration, making them ideal for long-haul applications.
d. Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference:
Unlike copper cables, fiber optic patch cables are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by nearby power lines, machinery, or other electronic devices. This makes them highly reliable in environments with high EMI, such as industrial settings.
e. Enhanced Security:
Fiber optic cables provide a high level of security as they are difficult to tap into or intercept. Unlike copper cables, which emit electromagnetic signals that can be intercepted, fiber optic cables do not emit any signals that can be easily tapped, making them more secure for sensitive data transmission.
5. Applications of Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
a. Telecommunications:
Fiber optic patch cables are extensively used in telecommunications networks to connect central offices, telephone exchanges, and cell towers. They enable high-speed data transmission, voice calls, and internet connectivity.
b. Data Centers:
Data centers rely on fiber optic patch cables to establish fast and reliable connections between servers, storage devices, switches, and routers. These cables ensure efficient data transfers, reduce latency, and support the high bandwidth requirements of modern data centers.
c. Local Area Networks (LANs):
Fiber optic patch cables are increasingly being deployed in LANs to create high-speed connections between network switches, routers, and end-user devices. This enables faster file transfers, video streaming, and online gaming experiences.
d. CCTV and Surveillance Systems:
Fiber optic patch cables are ideal for transmitting video signals in CCTV and surveillance systems. They provide high-quality video feeds over long distances without degradation, ensuring effective monitoring and security.
e. Industrial Automation:
In industrial automation applications, fiber optic patch cables enable reliable communication between various sensors, controllers, and equipment. They can withstand harsh environments, electromagnetic interference, and long transmission distances, making them suitable for industrial settings.
6. How to Choose the Right Fiber Optic Patch Cable?
a. Consider the Fiber Type:
Determine whether you require single-mode or multi-mode fiber optic patch cables based on the distance and bandwidth requirements of your application.
b. Determine the Connector Type:
Choose the appropriate connector type (SC, LC, ST, MTP/MPO, etc.) based on the devices you need to connect and the compatibility of their ports.
c. Select the Appropriate Cable Length:
Measure the distance between the devices you want to connect and choose a cable length that allows for flexibility and proper cable management.
d. Assess the Environment and Application:
Consider the environmental factors, such as temperature, moisture, and exposure to chemicals, to select cables with appropriate jacket materials and protection levels.
e. Verify Compliance with Industry Standards:
Ensure that the fiber optic patch cables you choose comply with relevant industry standards, such as ANSI/TIA-568-C, ISO/IEC 11801, or Telcordia GR-326.


7. Care and Maintenance of Fiber Optic Patch Cables:
Fiber optic patch cables are an essential component of optical fiber networks, as they provide the connection between devices and enable the transmission of data. To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of these cables, proper care and maintenance are crucial. Here are some important considerations:
a. Handling:
When handling fiber optic patch cables, it’s important to be gentle and avoid excessive bending or twisting. Excessive force or stress on the cable can cause damage to the delicate fibers inside. It’s best to hold the connector and avoid pulling or tugging on the cable itself.
b. Cleaning:
Regular cleaning of fiber optic patch cables is necessary to remove dust, dirt, and other contaminants that can degrade the signal quality. Use lint-free wipes or cleaning sticks specifically designed for fiber optic connectors. Avoid using cotton swabs or materials that can leave fibers or residue on the connectors. Clean both ends of the cable before connecting to devices.
c. Inspection:
Regular inspection of fiber optic patch cables is essential to identify any signs of damage or wear. Check for any visible cracks, breaks, or bent connectors. Also, inspect the cable ends for any signs of contamination or damage. If any issues are found, the cable should be replaced or repaired by a qualified professional.
d. Storage:
Proper storage of fiber optic patch cables is important to prevent damage. Cables should be coiled loosely and stored in a clean and dry environment. Avoid placing heavy objects on top of the cables or exposing them to extreme temperatures or humidity. It’s also recommended to use cable management solutions, such as cable ties or racks, to keep the cables organized and prevent tangling.
e. Avoid Excessive Length:
Excessive length of fiber optic patch cables can cause signal loss or degradation. It’s best to use the appropriate length of cable required for the specific connection. If longer distances are required, consider using fiber optic patch panels or fiber optic extenders instead of excessively long patch cables.
f. Proper Cable Routing:
When routing fiber optic patch cables, it’s important to avoid sharp bends or tight turns. Excessive bending can cause signal loss or even break the fibers inside the cable. Use cable management solutions, such as cable trays or raceways, to ensure gentle bends and proper support for the cables.
g. Professional Maintenance:
While regular care by the end-users is important, it’s also recommended to have professional maintenance and inspection of fiber optic patch cables periodically. This can help identify any potential issues or degradation before they cause significant problems. Professional technicians have the necessary tools and expertise to perform thorough testing and analysis of the cables.


8. Summary
Optical fiber experts are professionals with extensive knowledge and expertise in the field of optical fiber technology. They specialize in the design, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of optical fiber networks.
These experts are well-versed in the various components and systems involved in optical fiber communication, including fiber optic cables, connectors, splices, and transceivers. They understand the principles of light transmission through fiber optics and are familiar with the different types of optical fibers, such as single-mode and multi-mode fibers.
Optical fiber experts are skilled in performing fiber optic network installations, ensuring that the cables are properly laid out and terminated to achieve optimal performance. They have the necessary tools and equipment to splice and connect fibers, as well as test and measure the quality of the optical signals transmitted through the network.
In addition to installation, optical fiber experts are responsible for maintaining and troubleshooting optical fiber networks. They have a deep understanding of the potential issues that can arise in fiber optic systems, such as signal loss, attenuation, and dispersion. They have the expertise to identify and rectify these problems to ensure the smooth operation of the network.
Optical fiber experts also stay updated with the latest advancements in optical fiber technology and industry standards. They are knowledgeable about emerging trends, such as high-speed data transmission, fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) networks, and fiber optic sensors.
Overall, optical fiber experts play a crucial role in the deployment and maintenance of reliable and efficient optical fiber networks. Their expertise is essential in ensuring the seamless transmission of data, voice, and video signals over long distances.