Installing a Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network to support 5G technology requires careful planning and implementation to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are some best practices to consider for the installation of a 5G network on FTTH:
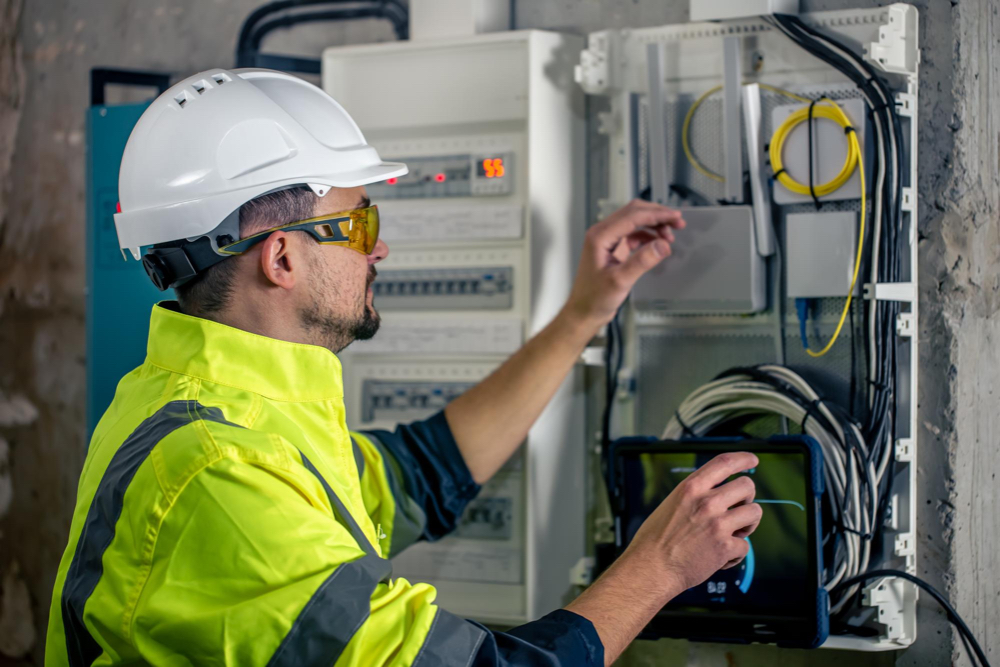


Network Design:
a. Conduct a thorough site survey and analysis to determine the optimal placement of fiber optic cables, taking into account factors such as proximity to 5G cell towers, projected user density, and coverage requirements.
b. Design the network with scalability in mind to accommodate future growth and increased bandwidth demands.
c. Use high-quality fiber optic cables capable of supporting high-speed data transmission and low-latency connections.
Fiber Optic Cable Installation:
a. Use appropriate methods to install fiber optic cables, such as aerial, underground, or direct burial, depending on the environmental and regulatory factors.
b. Employ proper cable management techniques, including ensuring minimum bend radius and avoiding sharp bends to prevent signal loss.
c. Conduct regular inspections and tests during and after cable installation to check for any damage and to verify signal integrity.
Fusion Splicing:
a. Use fusion splicing as the preferred method for connecting fiber optic cables. Fusion splicing offers lower insertion loss and higher reliability compared to mechanical connectors.
b. Follow industry standards and guidelines for fusion splicing to ensure proper alignment and protection of the fiber cores.
c. Perform comprehensive testing using an Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) to verify the integrity and performance of fusion spliced connections.
Power Management:
a. Ensure adequate power supply for both the FTTH network equipment and 5G cell towers. This includes implementing backup power systems and surge protection mechanisms to maintain network continuity during power outages.
b. Consider using power-saving technologies, such as Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) and Power over Ethernet (PoE), to optimize power consumption and reduce operational costs.
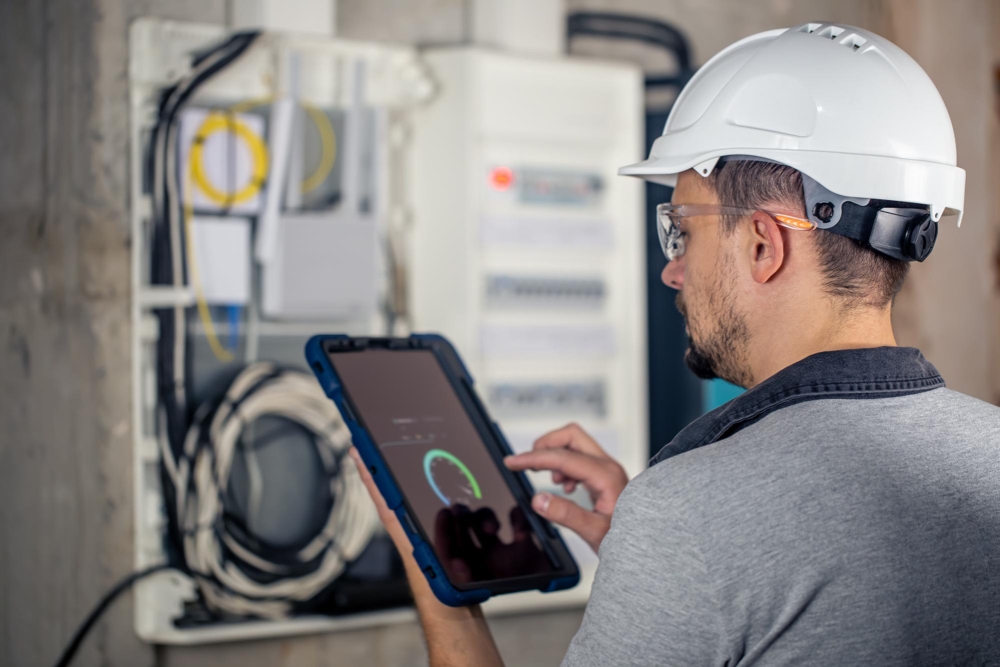


Fiber Connectors and Termination:
a. Use high-quality fiber connectors, such as SC or LC connectors, to ensure reliable and low-loss connections.
b. Invest in a proper fiber termination kit that includes epoxy or anaerobic adhesives, polishing films, pads, and connectors suitable for 5G network requirements.
c. Conduct regular inspections and cleaning of fiber connectors to prevent dirt and debris accumulation, which can cause signal degradation.
Network Testing and Maintenance:
a. Perform comprehensive testing of the FTTH network using specialized equipment and software to validate performance, identify potential issues, and optimize network configuration.
b. Regularly monitor the network performance, including latency, throughput, and signal quality, to ensure consistent delivery of high-speed and low-latency connectivity.
c. Implement proactive maintenance practices, including scheduled cleaning of fiber connectors, regular software and firmware updates, and periodic equipment checks to avoid network disruptions.
Collaboration with 5G Service Providers:
a. Collaborate closely with 5G service providers to ensure alignment between the FTTH network and 5G infrastructure.
b. Establish clear communication channels and workflows to facilitate efficient troubleshooting and problem resolution.
c. Stay updated with the latest industry standards, technological advancements, and service provider requirements to ensure compatibility and interoperability with 5G networks.
By following these best practices, FTTH network installers can ensure robust and reliable infrastructure to support 5G technology, providing end-users with high-speed and low-latency connectivity for their diverse digital needs.
Expanded Information: Industrial Internet Oriented 5G TSH Practice and Prospect – 2023 white paper
Powered By EmbedPress
Get this Full White Paper in PDF , email us.