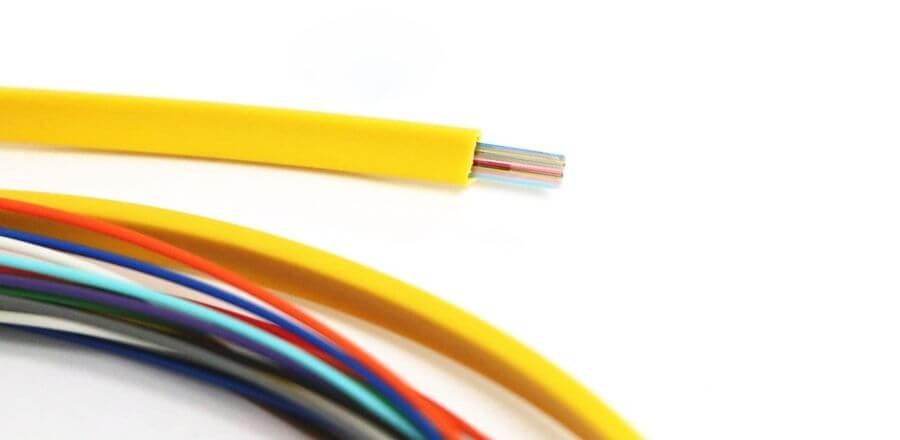
Ribbon fiber optic cable refers to a fiber optic cable in which the optical fiber in the cable adopts an optical fiber ribbon structure, while the optical fiber in the cable that is not an ribbon fiber optic cable has a discrete optical fiber structure. The fiber optic ribbon is a thin flat ribbon formed by curing 4 to 24 optical fibers in parallel.
Ribbon fiber optic cables are often referred to as “ribbon cables”, but flat optical cables are true ribbon cables, for their appearance is like a ribbon.
Ribbon Fiber Cable Structure
Ribbon fiber optic cable can be divided into layer stranded type, skeleton type and central tube type in terms of cable structure.
Layer Stranded
The structure of the stranded optical fiber ribbon cable is basically the same as that of the ordinary layer stranded loose tube fiber cable. The optical fiber ribbon in the cable mainly has 12 cores, 6 cores, and 4 cores. It’s currently the most used structure type of ribbon fiber optic cable.
Skeleton Type
The optical fiber ribbon in the cable is generally 4 core or 6 core, which is a water-blocking dry structure, which means no grease in the cable. The skeleton ribbon fiber cable is suitable for vertical wiring in buildings for each floors to cut out and splicing.
This skeleton structural characteristics determine its strong rigidity and it is difficult to bend during construction. However some carrier recommend it for it is a dry structure. In fact, the layer stranded optical cable can also be made into dry or semi-dry water resistance structure.
Central Tube
The optical fiber ribbon in the cable is generally 12 cores and 24 cores. The central tube optical cable has the characteristics of light weight, small diameter and low cost. If the fiber count of cores of the optical cable is not too many, it should be a better choice in optical communication network.
It is difficult to control the excess optical fiber length, and at extreme temperatures fiber failure might happen in the central tube optical cable. But the temperature adaptability of central tube optical fiber cable is not that bad too, in fact it can fully meet the requirements of most scenarios.
Ribbon Fiber Features
High Splicing Efficiency
When the ribbon fiber optic cable is spliced by a ribbon optical fiber fusion splicer, the optical fibers of one ribbon fiber cable can be spliced at one time. Thereby it greatly improves the efficiency of optical fiber splicing. The more the number of cores in each optical fiber ribbon, the higher the efficiency of the connection. At the same time, the quality of the connection will be worse too.
Ordinary fiber optic cable is limited by the connection efficiency, the fiber count is generally not very large, and the maximum fiber count usually does not exceed 288 cores. While the number of cores of ribbon fiber optic cables is mainly affected by demand. Although the current maximum is 576 cores, ribbon fiber cables with more than 576 cores will be used in large numbers in the future.
However, when the ribbon fiber optic cable is spliced with discrete optical fibers, or optical fiber ribbons with different fiber counts, the optical fiber ribbon needs to be torn apart into individual optical fibre for splicing, which is more troublesome than the splicing of ordinary optical cables.
Large Optical Splice Loss
Since the optical fiber ribbon cannot be accurately aligned during the splicing of the optical fiber ribbon, the splicing attenuation is greater than that of a single core.
Larger Diameter For Small Fiber Count
When the fiber count of the fiber optic cable is less than 144 cores, the outer diameter of the ribbon fiber optic cable is larger than that of the ordinary optical fiber cable.
Small Investment
The investment difference between the use of ribbon fiber optic cable and ordinary fiber cable in the optical communication network is mainly reflected in two aspect
1. Fiber optic cable price
From the perspective of production costs, there are a little more processes for the production of optical fiber ribbons and cables, and the cost will be a little higher. However, the price of fiber optic cable is often determined by the purchase volume and the competitive market. At present, as the use of ribbon fiber optic cable increases, the unit prices is getting closer and closer to those of ordinary optical cables.
2. Optical splicing cost
Because of the high splicing efficiency of the ribbon fiber optic cable, the splicing cost of each joint is lower. And the greater the fiber count of the ribbon fiber, the more obvious this advantage.
On the whole, the cost of using ribbon fiber optic cable in the optical communication network is slightly lower than that of using ordinary optical cable.
Advantages
- High connection efficiency
- Slightly lower cost
Disadvantages
- Need to be equipped with a fusion splicer with ribbon fiber fusion splicing capability
- High splicing attenuation
- Low efficiency when splicing with ordinary optical cables or optical fiber ribbons with different fiber count
Application Environment
Ribbon fiber optic cables are recommended to be used in large and medium-sized metropolitan area networks with a large number of fibre cores (not less than 72 cores). Such as the core network of the metropolitan area optical cable and the backbone section of the access network.
It is not suitable for using ribbon fiber cable in trunk optical communications, other optical fiber system sections with a relay distance of more than 70km, access network lead-in sections, and other sections with small fiber cores.