Optical Fiber Manufacturing
It is divided into two main processes: optical fiber preform making and fiber drawing.




Optical Fiber Perform
The production of optical fiber preforms mainly includes MCVD (Modified Checmical Vapor Deposition), OVD (Outer Vapor Phase Deposition), and VAD (Vapor Phase Axial Deposition) processes. MCVD is the most common manufacturing technique in use, which yields a low loss fiber well suited for long distance communication fiber optic cables. Therefore, we will cover the MCVD process in this article.
Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition (MCVD)
The MCVD (Modified Chemical Vapor Deposition) process was developed by Bell Labs in 1974. It introduces a gaseous mixture composed of SiCl 4 (silicon chloride), GeCl 4 (germanium chloride) and other chemical substances into the quartz glass tube (cladding). And rotates while heating outside the quartz tube to oxidize silicon and germanium to form SiO2 (Silica) and GeO2 (germanium dioxide), which will reside in the quartz tube to form the main part of the optical fiber.
The refractive index, expansion coefficient, and melting point of the optical fiber can be controlled by the component concentration of the gaseous mixture. After the optical fiber preform has cooled, it is subjected to a quality (refractive index) test.
Optical Fiber Drawing
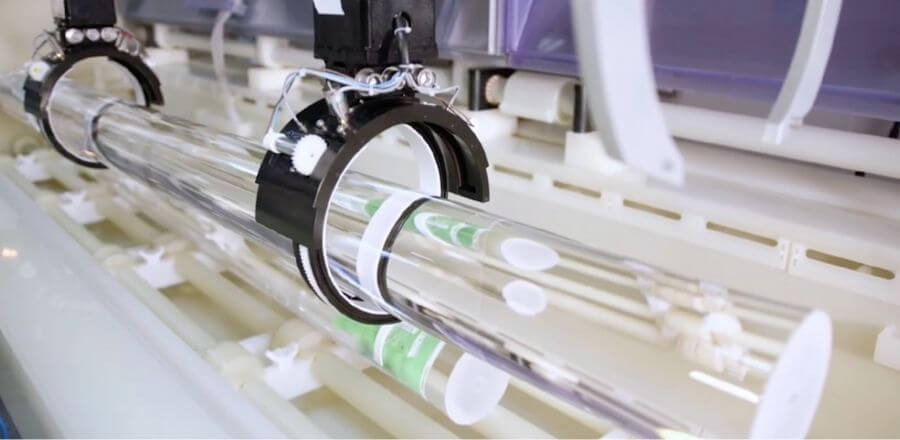
Optical fiber drawing refers to the operation process of puting the optical fiber preforms in to a vertical fiber drawing system, where fiber preforms are heated and melted by a certain heating device, and then drawn into small optical fibers with a diameter that meets the requirements. And the core/clad diameter ratio and refractive index distribution of the optical fiber are kept unchanged.
Fiber Drawing Tower
Optical fiber preform is put into a fiber drawing tower. A fiber drawing tower can be more than 10 meters high. Optical fiber preform is drawn into an optical fiber with a thickness of 125μm and coated with layers of resin for protection.
Furnance
There is a graphite furnace in the fiber drawing tower, which can generate a high temperature of 17000- 2200℃ to soften the preform. And then it is wound by a drawing wheel to draw a slender optical fiber. The drawing tower has an information feedback system, which is used to feedback the furnace temperature and winding speed, etc., so as to accurately control the fiber diameter through the laser micrometer.
Coating
The 125μm fiber drawn from the preform is thermally deformed, but there are still micro-cracks on the surface of the bare fiber. Once it is exposed to the atmosphere, the OH- in the atmosphere will cause the micro-cracks to expand. And prolonged exposure will cause the fiber to break.
In order to enhance the strength of the optical fiber, a thin layer of resin should be coated on the optical fiber in time during the drawing process and dried in time to avoid this and mutual adhesion.
Following Tests
After the drawing is completed, the finished optical fiber also needs to be tested. There are mainly tests for tensile strength, refractive index, fiber structure, attenuation, information carrying capacity (bandwidth), dispersion, operating temperature and humidity range, etc.
This is how optical fibers are made. It is this little glass filament that has completely changed our life today.