Optical Fibre
Therefore, optical fibre is a very convenient tool for signal transmission. A slender optical fiber inside the fiber cable can replace more than a thousand physical communication lines to complete a large number of network access and long-distance communication tasks.
Optical Fibre Advantage
The 8 major advantages of optical fiber transmission are as follows:
- High sensitivity, free from electromagnetic noise interference.
- Small size, light weight, long life and low price.
- Insulation, high pressure resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, suitable for work in special environments.
- The geometric shape can be adjusted according to environmental requirements, and the signal transmission is easy.
- High bandwidth, large communication volume, small attenuation, and long transmission distance.
- The signal crosstalk is small and the transmission quality is high.
- High confidentiality.
- It is convenient to lay and transportation.
So, how does optical fiber have the above major advantages?
3 Fiber Core Types
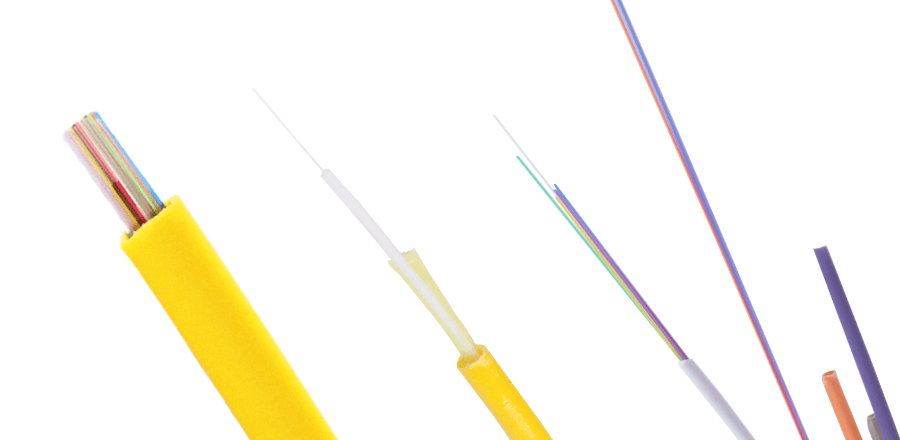
Optical fibers are made of glass that transmits optical signals through internal total reflection. The standard diameter of glass optical fiber is 125 microns (0.125 mm), and the surface is covered with a resin protective coating with a diameter of 250 microns or 900 microns. The central part of the glass fiber that transmits light is called the “core”, and the surrounding cladding has a lower refractive index than the core, which limits the loss of light.
Quartz glass is very fragile, so it is covered with a protective coating. There are usually three typical optical fiber coatings.
Loose Tube Optical Fibre
Loose tube optical fibre, or primary coated optical fiber, is an optical fiber coated with a UV curable acrylic resin coating with a diameter of 0.25 mm. Its diameter is very small, which increases the density of optical fibers that can be accommodated in the fiber optic cable, and it is widely used.
Tight Buffer Fiber
It is also known as secondary coating fiber or semi-tight buffer fiber. The surface of the optical fiber is covered with a thermoplastic resin with a diameter of 0.9 mm. Compared with the 0.25 mm optical fiber, it has the advantages of being more robust and easy to operate. It is widely used in local area network (LAN) cabling and fiber optic cables with a small number of fiber count.
Ribbon Fiber
Ribbon fiber are optical fibers processed by plurality of single optical fibers through coloring, stacking into ribbons. Each ribbon can consist of 4, 8, 12 or 16 fibers with different colors, and the number of a ribbon fiber cable can reach 1,000 core. The ribbon optical fiber improves the efficiency of the connector assembly and facilitates multi-core fusion, thereby improving the work efficiency.
Features of Ribbon Fiber
There are two types of ribbon fibers, encapsulated type and edge-bonded type. The former can withstand lateral pressure and the latter is thinner. The surface of the ribbon fiber is covered with UV-curable acrylic resin material. The coating layer can be easily removed by using standard optical fiber stripper pliers, which is convenient for multi-core fusion or take out a single optical fiber. Using a multi-core fusion splicer, ribbon fibers can be fused all at once and can be easily identified in fiber optic cable with a large number of optical fibers.
The spacing of optical fibers in the ribbon is 0.28mm (for 4, 8 fiber) and 0.3mm (for 12 and 16 fiber), which are neatly arranged. There is flatness in the vertical direction, that is, the deviation is required. And it should not be greater than 30, 40, 50um (depending on the number of optical fibers in the ribbon) to facilitate cluster (fusion splicing) connection. The optical fiber in ribbon uses the chromatogram in an orderly manner to facilitate correct identification during maintenance and connection.
Ribbon Fiber Application
The optical fiber ribbon is small in size, which can increase the package density of the optical fiber in the fiber cable, and can form a large number of cores, such as 320 to 3456 cores. It is suitable for the current rapidly developing optical fiber access network.